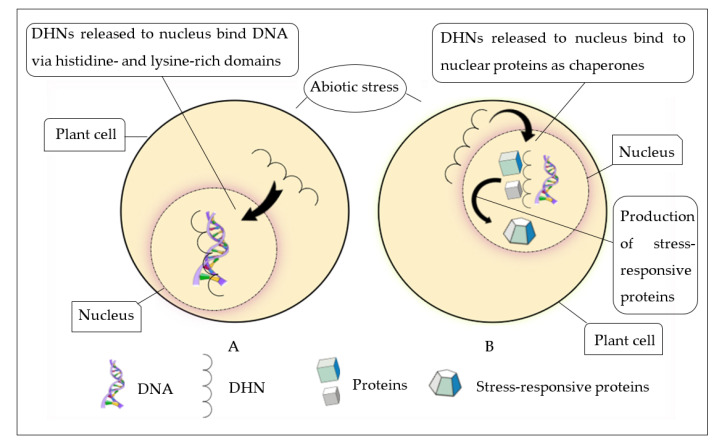
Figure 3.
Role of DHNs inside the nucleus of a cell (A—binds to DNA, B—binds to other protein molecules). (A) Nuclear-localized DHN under stress conditions binds to DNA because of the presence of DNA-binding domains (histidine and lysine), which may repair or protect the DNA from damage caused by abiotic stresses. (B) DHNs shield protein molecules through protein–protein interaction as chaperones in the nucleus and facilitate the production of stress-responsive proteins.