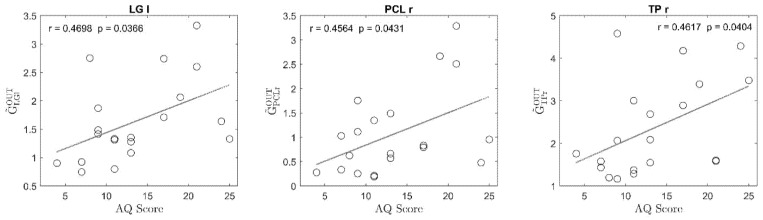
Figure 1.
Plot of the regression lines between the sum of the normalized connections exiting from a given region (output sum ) and the Autism Spectrum Quotient (AQ) score, obtained using data from the 20 participants. Only plots in the three regions that exhibit a correlation coefficient higher than 0.4, with a significant p value for the correlation and significant difference between the two classes, are shown. For each plot, the regression coefficient and the p value for testing the hypothesis of no-correlation are shown in the label. It is worth noting that to obtain these plots, the connection matrix for each participant was normalized so that the total sum of connection strength was as high as 100 (see Equations (4)–(6)); hence, for example, a value of 3 on the y-axis indicates that 3% of the total connections in the network are exiting from that particular ROI. Hence, the values in these plots reflects whether the connections leaving the ROI are stronger (high value) or weaker (low value) compared to the total sum of the connections in the same subject.