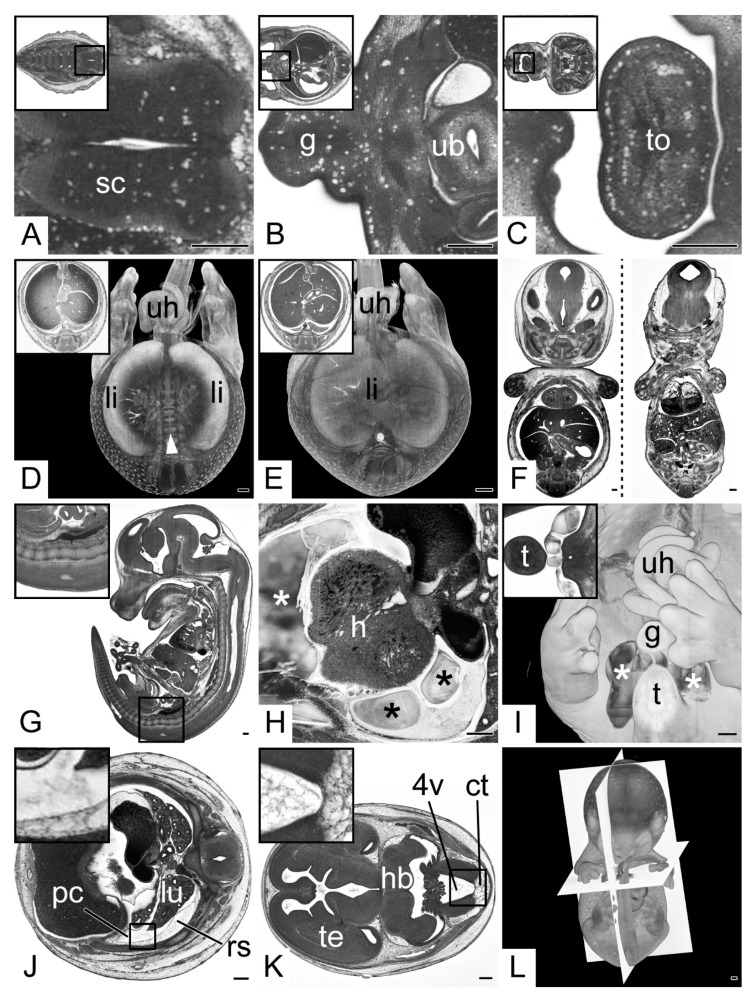
Figure 3.
Specimen processing and embedding artefacts. (A–C) Vacuoles in various tissues. Transverse HREM sections, ventral to the left. Inlays: overview. (A) Caudal segment of spinal cord (sc). (B) Genital region (g). (C) Tongue (to). Note the vacuoles following the tissue border between mucosa and muscle tissue. (D,E) Low tissue contrast inside liver (li). Semitransparent volume model transected at the height of the umbilical hernia (uh). Inlays: Transverse HREM sections. (D) Due to the low contrast of the liver, its center is not rendered and the underlying vertebral column (white arrow head) is visible. (E) control. (F) Lateral deformation, coronal resections. Deformed embryo on the right showing lateral compression and flattening. Control on the left. (G) “Pseudolordosis” of the sacral spine, sagittal resection, ventral to the left. (H,I) Cavities (*) in resin block (H) Cavities (*) inside the pericardial sac near the heart (h). Transverse HREM section, ventral to the left. (I) Cavities (*) outside the embryo body, near the base of the tail (t). A 3D model from ventral. Inlay: Transverse HREM section. (J,K) Debris inside body cavities. Transverse HREM sections, ventral to the left. (J) Debris inside pleural cavity (pc). Compare the adjacent retropleural space (rs). (K) Debris in 4th brain ventricle (4v) compare the leptomeningeal connective tissue (ct). In addition, note the appearance of the telencephalic (te) ventricles. (L) Poorly aligned embryo. A 3D model strictly from ventral. Orientation planes as defined by the embedding block in white. Abbreviations: 4v: 4th ventricle, ct: leptomeningeal connective tissue, g: genitalia, h: heart, hb: hindbrain, pc: pleural cavity, rs: retropleural space, sc: spinal cord, t: tail, te: telencephalon, to: tongue, ub: urinary bladder, uh: umbilical hernia. When not stated otherwise, box indicates magnification in inlay. Scale bars = 250 µm.