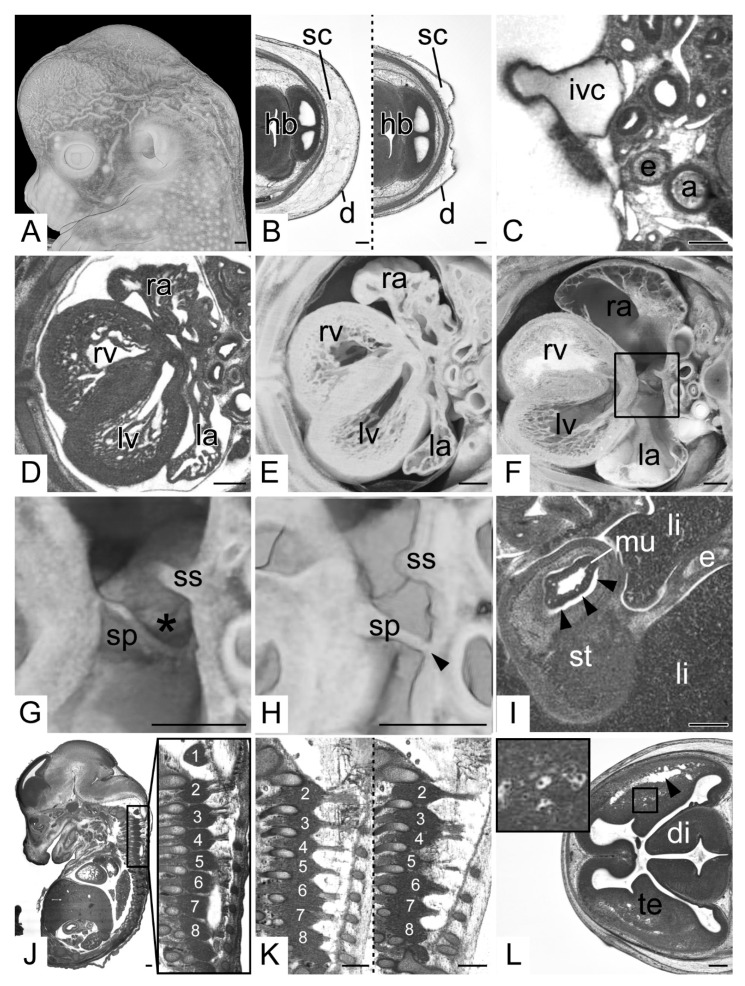
Figure 4.
Shrinkage artefacts. (A) Wrinkled skin. Volume model from left. (B) Thickness of the subcutis (sc). Transverse HREM sections, ventral to the left. (C) Cross section of the inferior vena cava (ivc). Compare shape to aorta (a). Transverse HREM section, ventral to the left. (D–F) Atrial appendages. (D) Transverse HREM section, ventral to the left. (E) Transected 3D model. (F) Control. Note the wall shrinkages and cavity dimensions (ra, la). (G,H) Foramen ovale (asterisk). Transected semitransparent volume models. (G) is a magnification of (F) and serves as control. (H) Septum primum (sp) touching the dorsal atrial wall (arrow head). The foramen ovale appears as if closed. (I) Artificial detachment of stomach (st) mucosa (mu). Transverse HREM section (J,K) Cervical spinal ganglia (1–8). Sagittal resections, ventral to the left. (J) Demarcated ganglion material. (K) Connected ganglia (2–8) in a wildtype (left side) and a 4933434E20Rik mutant (right side). Note the separated dorsal roots in the wildtype and the mingled dorsal roots of 3 and 4 in the mutant. (L) Spongy appearance of brain tissue. Elongated cavities profound to the superolateral cerebral cortex (arrow head) and cavities surrounding intracerebral blood vessels. Inlay: Magnification of cavities around blood vessels. Abbreviations: 1–8: cervical dorsal root ganglion 1–8, a: aorta, d: dermis, di: diencephalon, e: esophagus, hb: hindbrain, ivc: inf vena cava, la: left atrium, li: liver, lv: left ventricle, mu: mucosa, ra: right atrium, rv: right ventricle, sc: subcutis, sp: septum primum, ss: septum secundum, st: stomach, te: telencephalon. Scale bars = 250 µm.