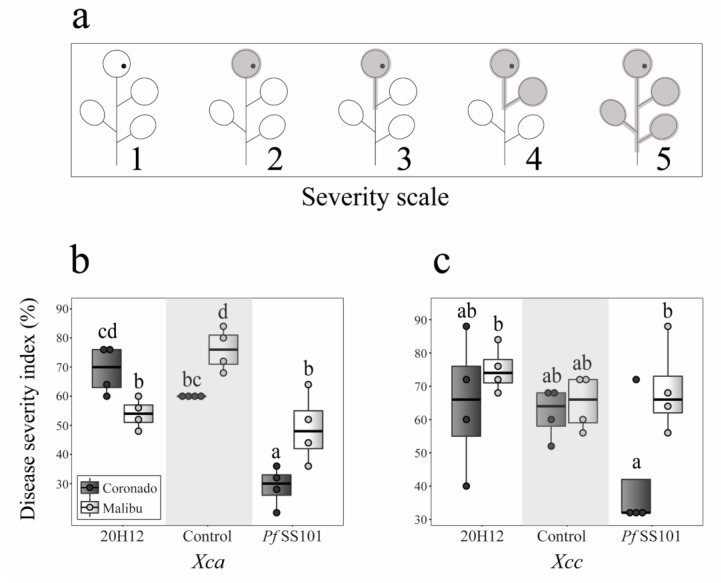
Figure 2.
Rhizobacteria-mediated systemic resistance in two Broccoli cultivars, Coronado and Malibu, against the bacterial leaf pathogens. Disease severity was scored on an ordinal scale from 0 to 5, where 1 = no necrosis or migration, 2 = full infection of the treated leaf, 3 = migration of the infection to the leafstalk of the treated leaf, 4 = infection of the neighboring leaf, and 5 = infection of the entire seedling (a) (see Supplementary Materials Figure S1 for further details). Details on the conversion of the ordinal scales to disease severity index is provided in the Material and Methods section. Impact of priming roots of Broccoli cultivars with rhizobacteria on severity of leaf disease caused by Xanthomonas campestris pv. armoraciae (Xca) (b) and Xanthomonas campestris pv. campestris (Xcc) (c). Prior to pathogen inoculation on the leaves, roots of each Broccoli cultivar were treated with P. fluorescens SS101 or its cysH-mutant 20H12 and incubated for 11 days. For the disease severity caused by Xca or Xcc, Broccoli seedlings from four biological replicates were individually scored (n = 20). Different letters above bars indicate statistically significant differences based on beta regression analysis followed by Tukey test (p < 0.05).