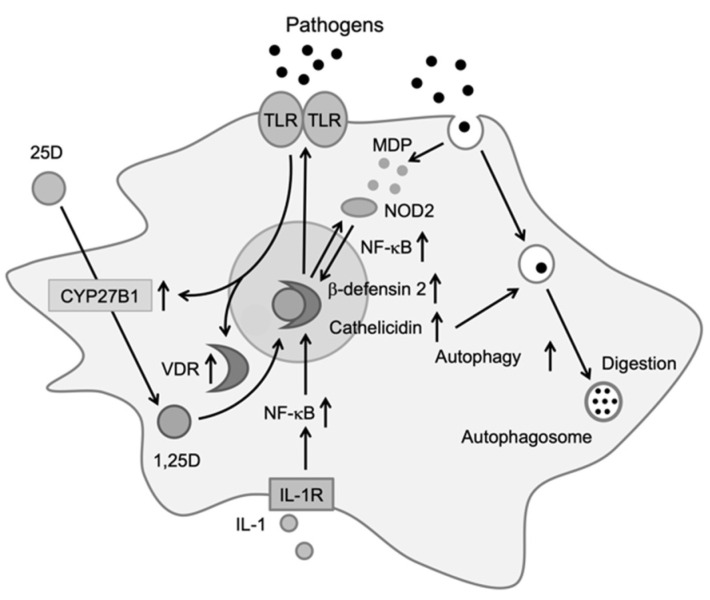
Figure 1.
Effects of vitamin D on immune cells. Activation of toll-like receptors by pathogens increases the expression of vitamin D receptor (VDR) and CYP27B1. Upon entering the cell, 25D is metabolized to 1,25D by CYP27B1. 1,25D then binds to VDR, which induces cathelicidin and β-defensin 2. Cathelicidin promotes antibiotic activity via autophagy [14].