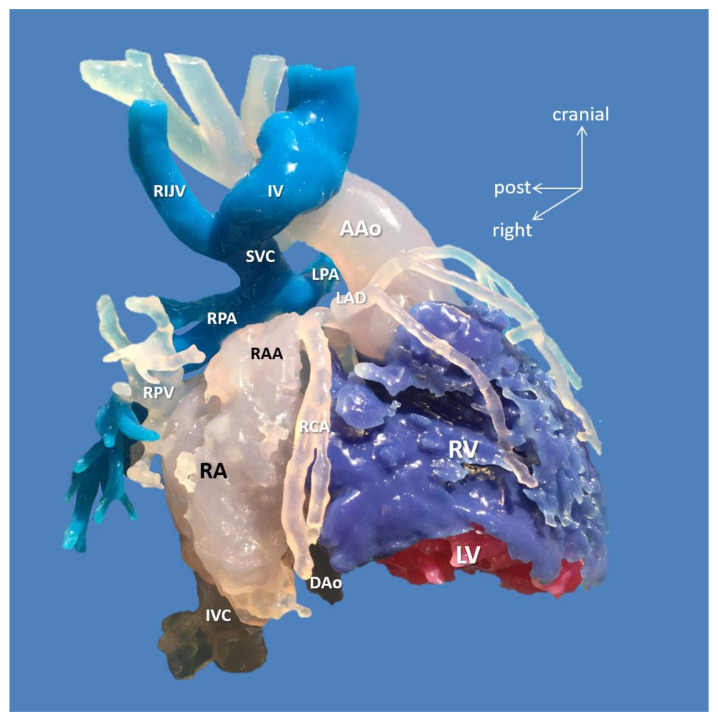
Figure 3.
3D-printed blood volume model of mesocardia, common atrium, criss-cross heart (supero-inferior ventricles), transposition of the great arteries, and pulmonary atresia, restrictive VSD and thrombus formation in the left ventricle; operated bidirectional superior cavopulmonary (Glenn) anastomosis (Case 15). Patient also had variant coronary artery anatomy: right coronary and left anterior descending arteries originated from left-hand facing posterior sinus, and a separate circumflex originated from right-hand facing anterior sinus. Modeling was indicated to assess the extent of the left ventricle thrombus and suitability for biventricular repair. The model did not reveal any possibility of connecting the left ventricle to the aorta. Patient underwent univentricular staging: total cavopulmonary connection with intracardiac conduit, LV thrombus removal and VSD enlargement. Abbreviations: AAo: ascending aorta, DAo: descending aorta, IV: innominate vein, IVC: inferior vena cava, LAD: left anterior descending coronary artery, LPA: left pulmonary artery, LV: left ventricle, RA: right atrium, RAA: right atrial appendage, RCA: right coronary artery, RIJV: right internal jugular vein, RPA: right pulmonary artery, RPV: right pulmonary vein, RV: right ventricle, SVC: superior vena cava.