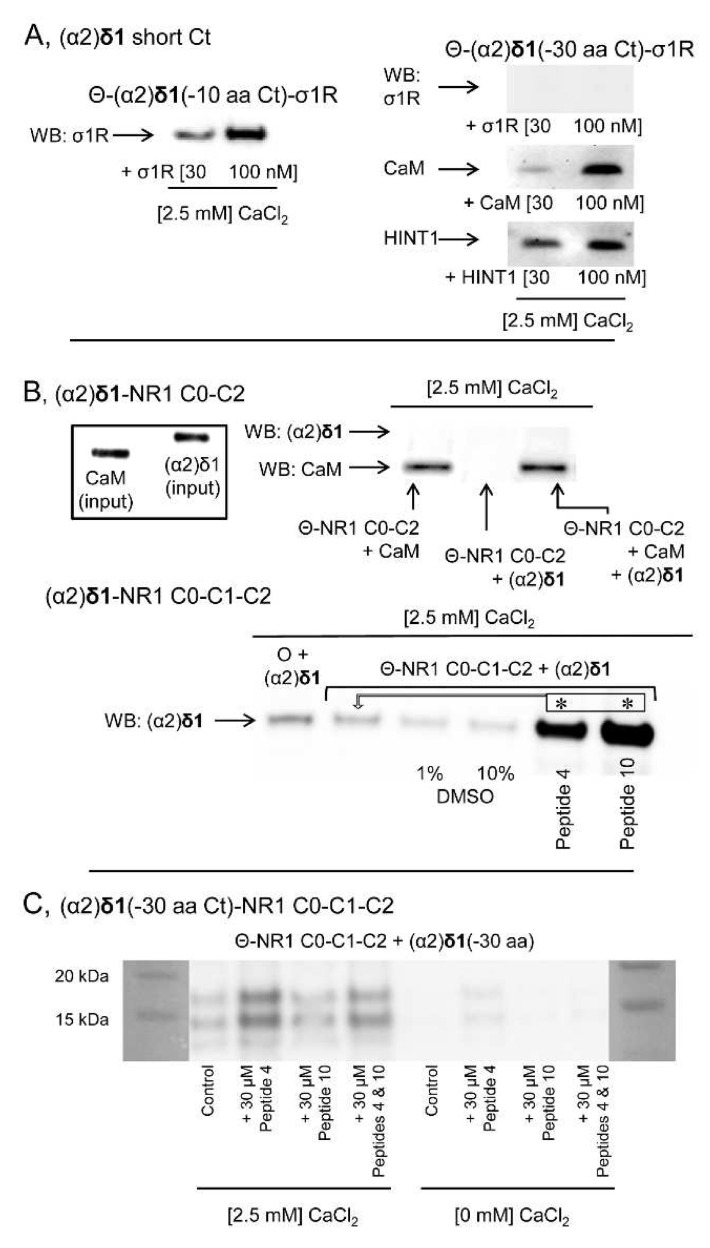
Figure 8.
The C terminal sequence of the (α2)δ1 peptide binds to σ1Rs and NMDAR NR1 C1 subunits. (A) Immobilized (α2)δ1 C terminal truncated sequences (–10 or –30 aa) were incubated with σ1Rs, CaM or HINT1 proteins (100 nM) in the presence of CaCl2 (2.5 mM). The proteins bound to agarose-(α2)δ1 were separated from the unbound fraction by several cycles of washing-resuspension, the bound proteins were detached in 2× Laemmli buffer containing β-mercaptoethanol, resolved by SDS-PAGE and analyzed in Western Blots (WBs). (B) The (α2)δ1 peptide binds to the NR1 variant, which contains the cytosolic C1 segment. The cytosolic sequences of the NR1 C0-C2 and NR1 C0-C1-C2 variants (100 nM) were incubated with (α2)δ1 peptides in the presence of CaCl2 (2.5 mM). The agarose-bound proteins were detached, resolved by SDS-PAGE and analyzed in WBs. To facilitate the access of (α2)δ1 peptides to the NR1 C1, interactions were performed in the presence of 1 or 10% DMSO, with a peptide (30 μM) mapping to the C0 region (peptide 4, 849–858: QLAFAAVNVW) or the C1 region of the NR1 subunit (peptide 10, 879–888: TFRAITSTLA). The arrows refer to the comparison and * indicates significant difference relative to the control group: p < 0.05. (C) The peptides mapping to the C0 or C1 cytosolic region of the NR1 subunit did not promote binding of the truncated (–30 aa) (α2)δ1 peptides to the NR1 C1 subunits, either in the presence or absence of CaCl2 (2.5 mM: for further details see the Methods). O and Θ represent plain agarose and NHS-Sepharose®, respectively.