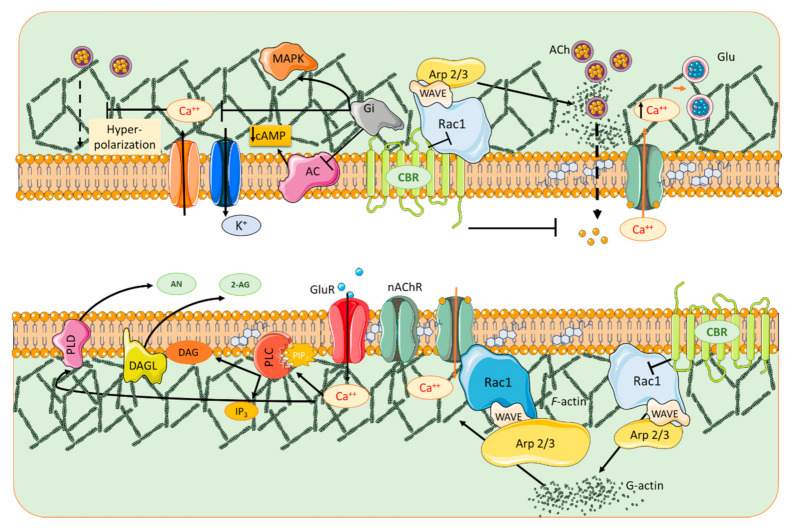
Figure 3.
Schematic diagram of a vomposite synapse summarizing the pre- and postsynaptic components participating in synaptic signaling dissected in this review. Glutamatergic (Glu) and cholinergic (α7 nAChR) activation promotes Ca2+ entry into the dendritic spine, inducing endocannabinoid (eCB) synthesis through hydrolysis of lipid precursors from the cell membrane. Cannabinoid receptor (CBR) activation in dendritic spines inhibits Rac1/WAVE/Arp 2/3 and limits the conversion of G actin to F-actin, whereas α7 nAChR promotes formation and maturation of dendritic spines through F-actin stability by activating the Rac1/WAVE/Arp2/3 signaling pathway. Phospholipase C (PLC) converts PIP2 into diacylglycerol (DAG) and in turn DAG lipase (DAGL) generates the eCB 2-AG. In parallel, phospholipase D (PLD) converts N-arachidonoyl phosphatidylethanolamine into the eCB AN. 2-AG and AN are liberated into the synaptic cleft and activate CBRs in the presynaptic compartment. Upon activation, CBRs stimulate Gi-protein and inhibit AC activity, membrane hyperpolarization ensues after the modulation of K+ and Ca2+ channels that inhibit neurotransmitter release from the presynaptic compartment. Finally, the mitogen-activated protein kinase (MAPK) pathway is stimulated. AC: adenyl cyclase; cAMP: cyclic AMP; ACh; acetylcholine; 2-AG, 2-arachidonyl glycerol.