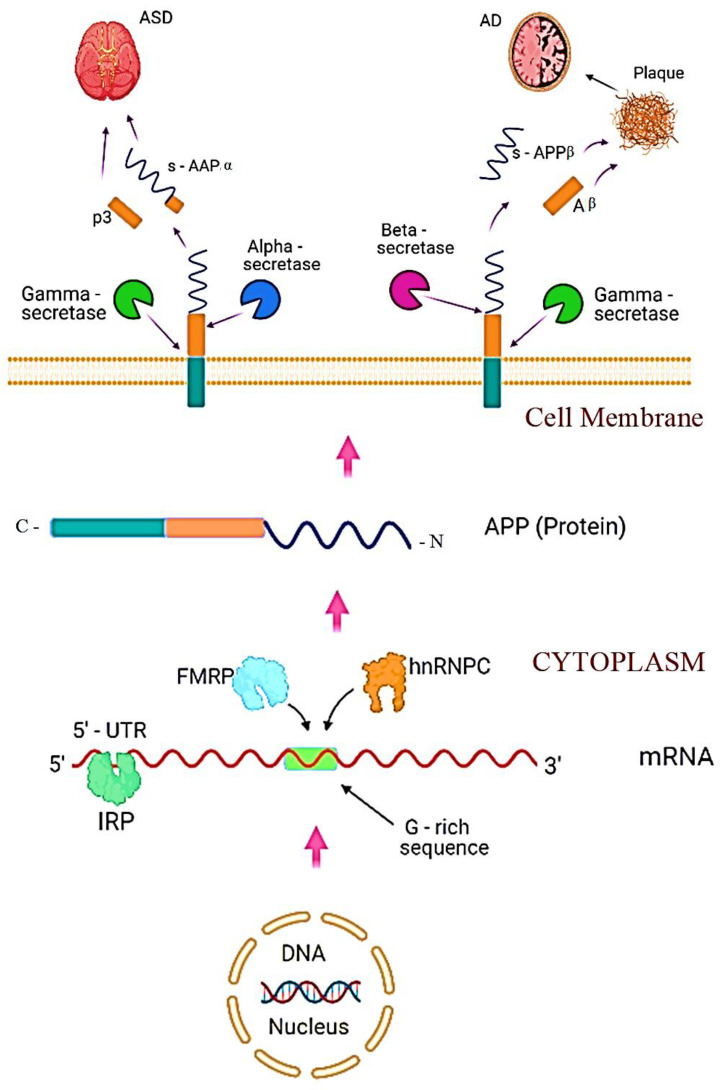
Figure 3.
Parallel yet divergent proposed mechanism of ASD and AD pathogenesis. Transport and translation of APP mRNA are well regulated by mRNA transport proteins and RNA binding proteins, such as IRPs and FMRP and miRNAs. There is a G-rich domain in the coding region of mRNA. FMRP and hnRNPC compete to bind this domain to suppress or enhance translation, respectively. APP is a transmembrane protein that is processed by combinations of α-, β-, and γ-secretases, resulting in different product combinations. p3 and s-AAPα promote ASD downstream, while s-APPβ and Aβ, in combination with other molecules, result in the formation of senile plaques and cause AD.