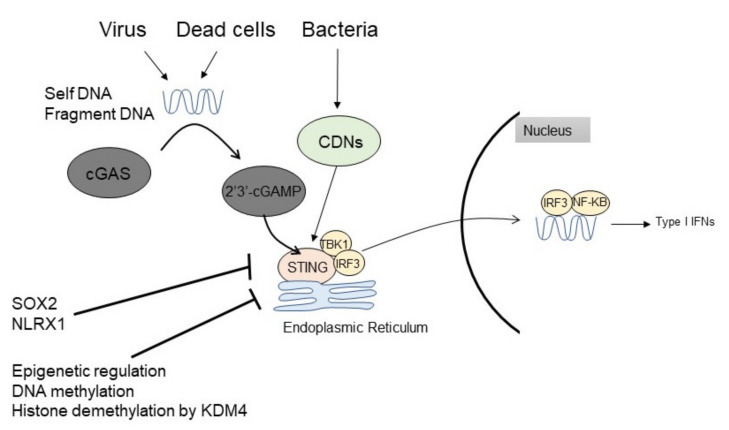
Figure 1.
Pathway of STING signaling and anti-tumor immunity. Cytosolic DNA triggers the activation of cGAS-cGAMP-STING signaling. Cytosolic DNA is detected by a DNA sensor protein, cGAS, which enhances the synthase of 2′3′-cyclic GMP-AMP (2′3′-cGAMP). cGAMP plays as a second messenger for the activation of STING. Bacteria can also generate CDNs and activate STING independently of cGAS. STING activates transcription factors IRF3 and STAT6 through TBK1 and promotes the gene transcription of type I IFN. DNA: deoxyribonucleic acid, cGAS: cyclic GMP-AMP synthase, CDNs: cyclic dinucleotides, STING: Stimulator of IFN genes; TBK1: tank binding kinase 1; IRF3: interferon regulatory factor 3, NF-kB: nuclear factor-kappa B; IFN: interferon; SOX: SRY-box transcription factors; NLRX1: NLR Family Member X1.