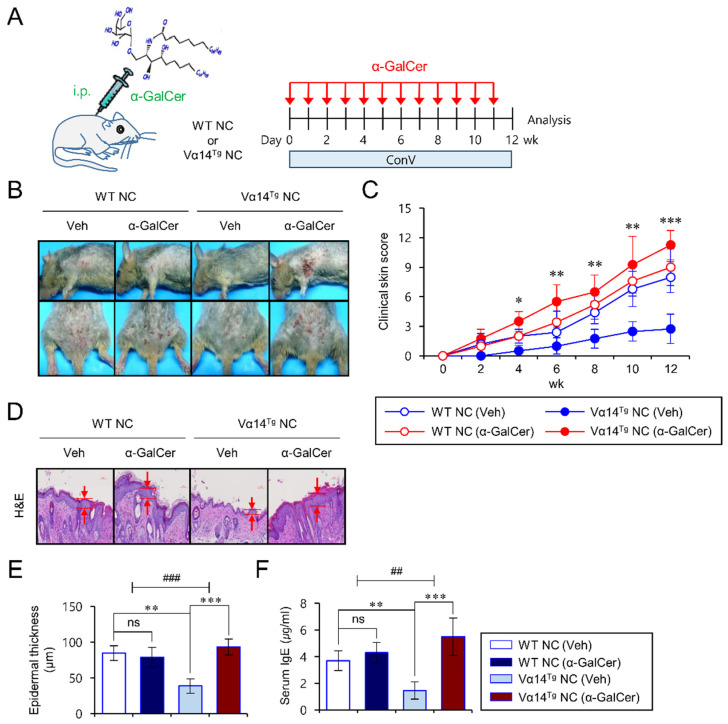
Figure 1.
Vα14Tg NC mice become susceptible to AD upon repeated α-GalCer treatment. (A) WT NC and Vα14Tg NC mice were i.p. injected with either Veh (n = 4) or α-GalCer (2 μg; n = 4) once per week from 6 weeks of age for a total of 12 weeks under conventional housing conditions to spontaneously develop AD. All the samples were prepared from mice at 12 weeks post transfer to conventional housing conditions for AD development. (B,C) The clinical symptoms were measured once a week to monitor the onset of AD. (D,E) The skins were prepared from WT NC or Vα14Tg NC mice. (D) Skin lesions were sectioned and stained with H&E. (E) The epidermal thickness was measured in 10 random high-power fields (400×) per sampled lesion. (F) Serum IgE levels were measured by ELISA. The mean values ± SD (n = 4–5 in A, B, C, D, E, and F; per group in the experiment; Student’s t-test; * p < 0.05, ** p < 0.01, *** p < 0.001) are shown. Two-way ANOVA (Vα14 TCR Tg × α-GalCer) showed an interaction between these two factors. One representative experiment of two experiments is shown (## p < 0.01 and ### p < 0.001).