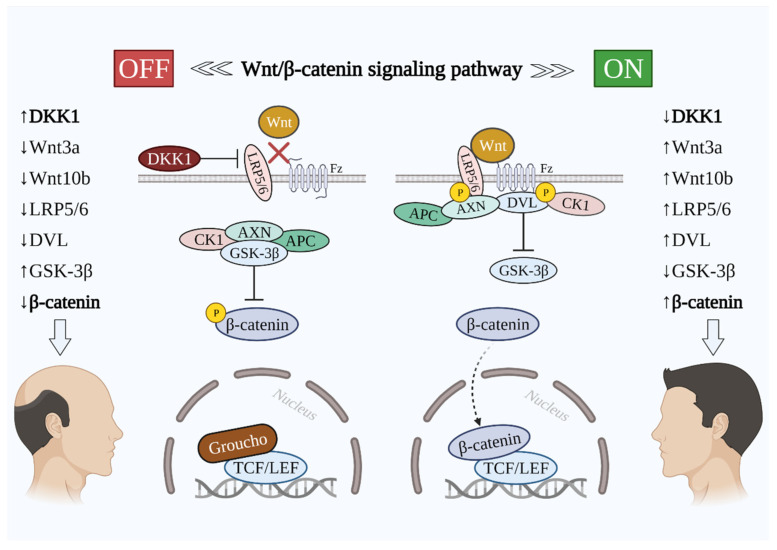
Figure 1.
The implication of key molecules in the Wnt/β-catenin signaling pathway in hair loss and growth. Wnt/β-catenin signaling pathway OFF (on the left side): DKK1 inhibits LRP5/6 and does not allow Wnt proteins to activate the signaling pathway. Destruction complex inhibits β-catenin and its translocation into the nucleus is prevented. Transcription of Wnt-targeted genes is hindered. Wnt/β-catenin signaling pathway ON (on the right side): Wnt binds to Fz and LRP5/6, which is followed by the phosphorylation of LRP5/6 intracellularly that leads to the DVL recruitment to Fz. β-catenin is then translocated into the nucleus and displaces Groucho. Transcription of Wnt-targeted genes takes place. Abbreviations: DKK1, dickkopf-related protein 1; Wnt, wingless and integrated-1; Fz, frizzled; LRP5/6, low-density lipoprotein receptor-related proteins 5/6; AXN, axin; GSK3-β, glycogen synthase kinase 3β; CK1, casein kinase 1; DVL, dishevelled; APC, adenomatous polyposis coli; TCF/LEF, T-cell factor/lymphoid enhancer factor.