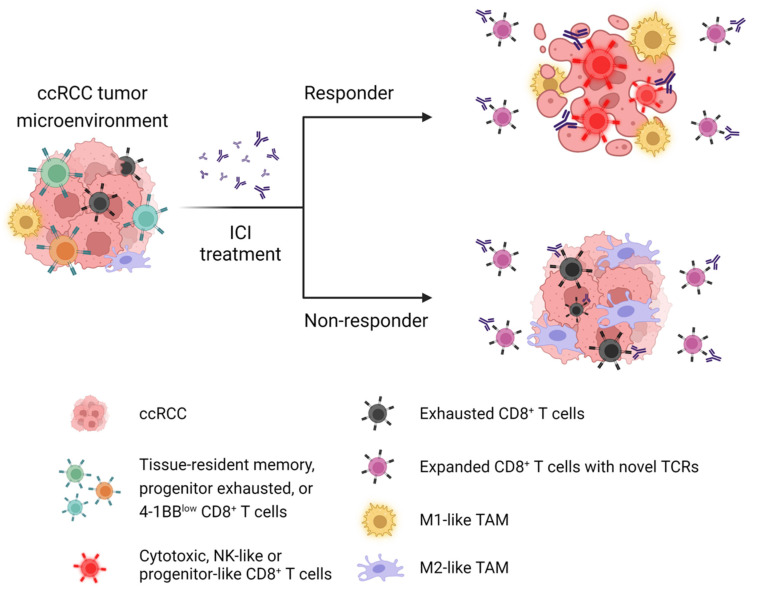
Figure 3.
Current concept of immunotherapy driving clinical response to ICI in patients with ccRCC. Pre-existing CD8+ T cell clones phenotyped by CD69+ZNF683+ TRM, progenitor exhausted, or 4-1BBlow are considered to have a critical role in favorable response to ICI in ccRCC patients. In responders, ICI-bound expanded CD8+ T cells exhibit cytotoxic, NK-like, or progenitor-like phenotypes. In contrast, non-responders had no clonal expansion of the tumor-reactive CD8+ T cell clones. In both responders and non-responders, pre-existing exhausted T cells are clonally expanded following ICI treatment. In ccRCC, clonal expansion of CD8+ T cells with novel TCRs are not associated with clinical response to ICI. Following ICI treatment, TAMs shift toward M1-like or pro-inflammatory phenotype in responders, whereas non-responders have skewed polarization of TAMs toward M2-like or anti-inflammatory phenotype in ccRCC tumor microenvironment. CD69, ZNF683, and CD103 are commonly expressed in CD8+ TRM cells. 4-1BBlow CD8+ T cells are highly enriched with progenitor exhausted signature. The tumor-reactive effector-like CD8+ T cells commonly express GZMA, GZMB, GZMK, PRF1, IFNG, NKG7, CCL3, CCL5, and CXCL13 genes, as well as co-inhibitory receptors, such as PD-1, TIM-3, LAG3, and TIGIT genes. Terminally exhausted phenotype is characterized by high expression of PD-1, LAG-3, TIM-3, CTLA-4, TOX, and CD39. M1-like TAMs are highly enriched with signatures of interferon signaling, antigen presentation, and proteasome function. M2-like TAMs are commonly characterized by high expression of HLA, APOE, C1QA, and TREM-2. Abbreviation: ccRCC; clear cell renal cell carcinoma, ICI; immune checkpoint inhibitor, TAMs; tumor-associated macrophages, NK; natural killer, TCR; T cell receptor.