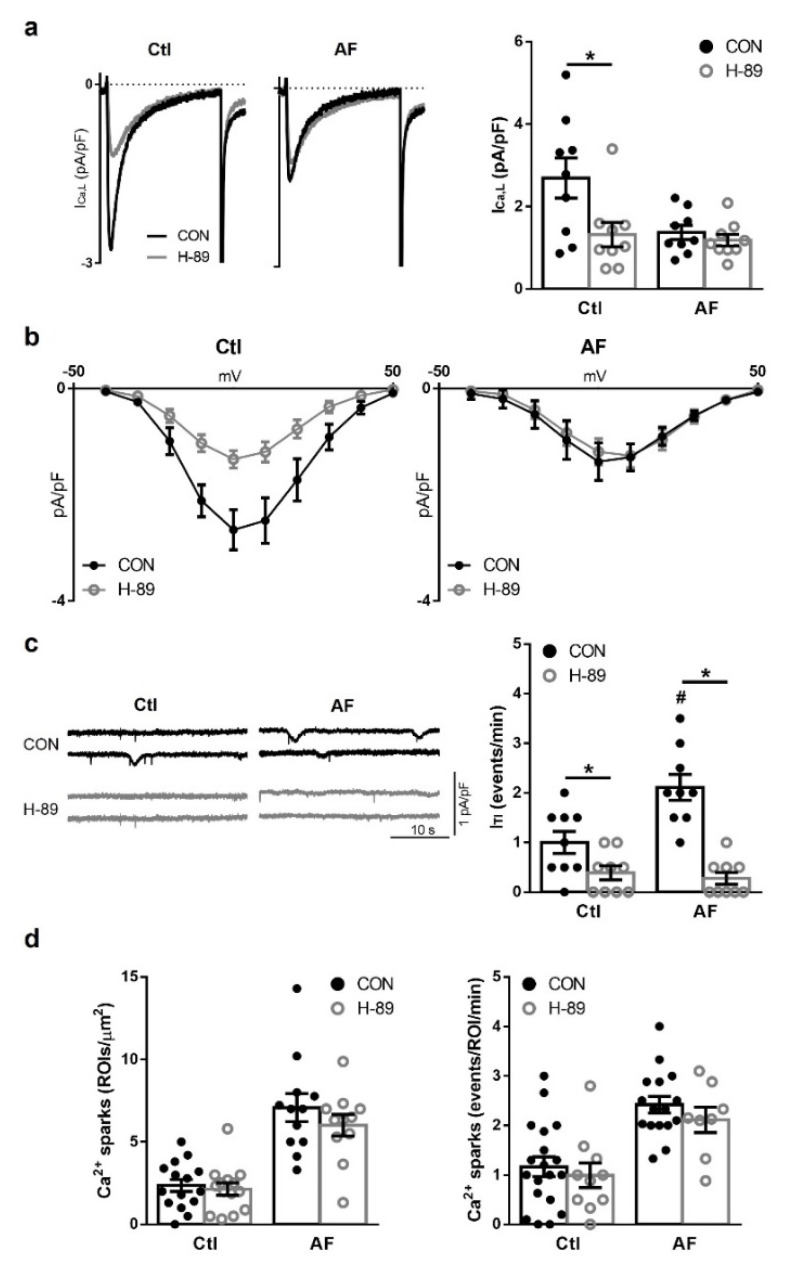
Figure 1.
Effect of protein kinase A (PKA) inhibition on ICa,L, ITI and sarcoplasmic reticulum (SR) Ca2+ load. (a) (left): Representative ICa,L recordings in myocytes from a patient in sinus rhythm (Ctl) and a patient with atrial fibrillation (AF) before (CON, black trace) and after exposure to the selective PKA inhibitor (H-89, 10 μM, grey trace). (right): Average effect of H-89 in Ctl and AF patients. (b) Mean effect of H-89 on the current-voltage relationship in Ctl and AF patients. (c) (left): Representative traces of spontaneous ITI recorded in Ctl and AF myocytes before and after exposure to H-89. (right): Mean effects of H-89 on the spontaneous ITI frequency in Ctl and AF patients. (d) Average effects of H-89 on Ca2+ sparks density (left) and frequency (right) before and after exposure to H-89. ROI: region of interest. Significant differences between treatments are indicated with * and between groups with #.