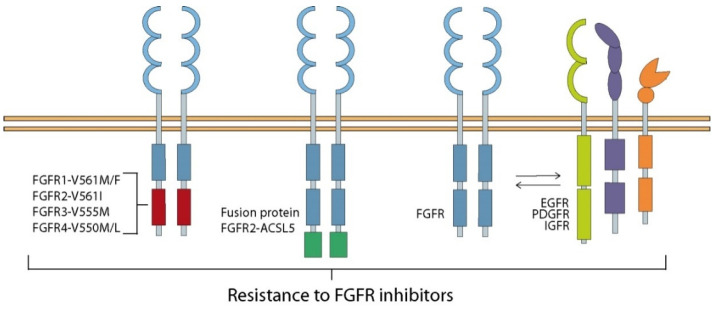
Figure 5.
Mutations and molecular cross-talks in the acquisition of resistance to FGFR inhibitors. The use of TKIs in cancer cells expressing FGFRs leads to the acquisition of gatekeeper mutations in the FGFR kinase domain (FGFR1-V561M/F, FGFR2-V561I, FGFR3-V555M, and FGFR4-V550M/L), which in turn desensitize cells to the inhibitor used and may also induce cross-resistance to other inhibitors. FGFR2-ASCL5 fusion leads to the development of resistance to LY2874455, an FGFR inhibitor that overcomes resistance caused by gatekeeper mutations. FGFR inhibition can also lead to the activation of other RTKs, including EGFR, PDGFR, and IGFR, which alternatively trigger downstream cell signaling and render cells insensitive to TKIs.