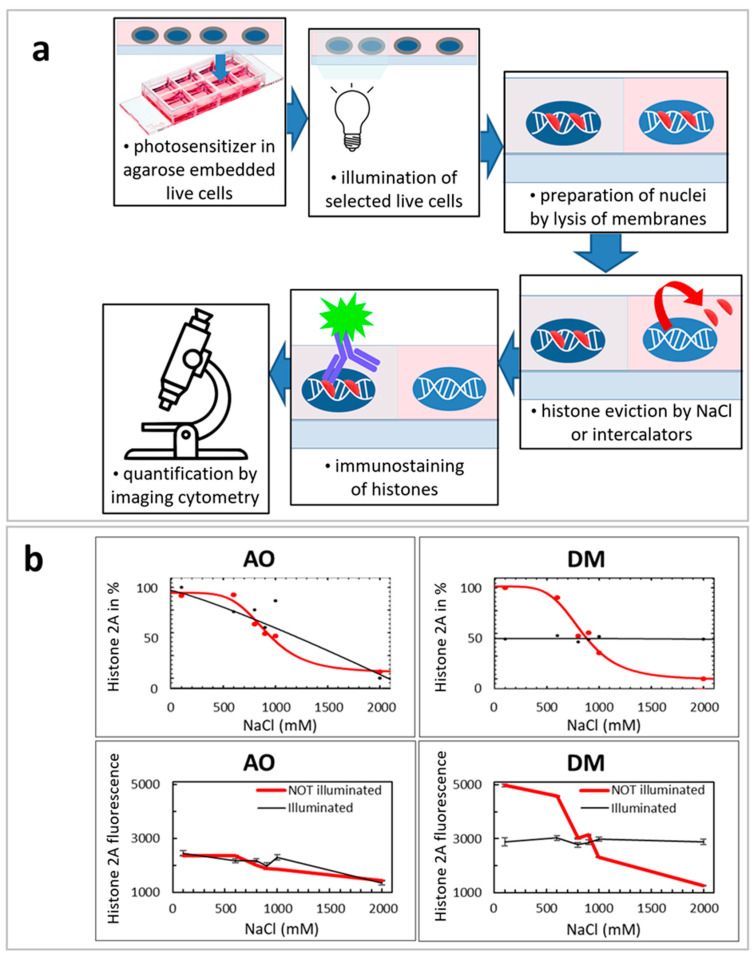
Figure 6.
Loss of histone H2A and photofixation in the chromatin. AO evicted more histone H2A from nuclei as a result of the light-induced nuclear DNA fragmentation. DM crosslinked more histone H2A to the chromatin in the illuminated HeLa cells. (a) Scheme of the modified QUINESIn method to detect chromatin integrity [24]. Histones are released from nuclei by applying high concentrations of salts unless the photo-treatment crosslinked proteins covalently to the DNA or other proteins. Anti-histone H2A antibodies were used to detect the presence of specific histones. (b) The amount of histone H2A was plotted versus the salt concentration. In the upper panels, the relative amount of histone H2A is given in percentages normalized to the no salt condition (100%). In the lower panels, raw data of the histone fluorescence are plotted on the ordinate in arbitrary units (mean ± SEM). The left panels show AO, while the right panels show DM sensitization. All black lines display the light treatment, while red curves label the absence of illumination. In this figure, we demonstrated one representative data set from three experiments.