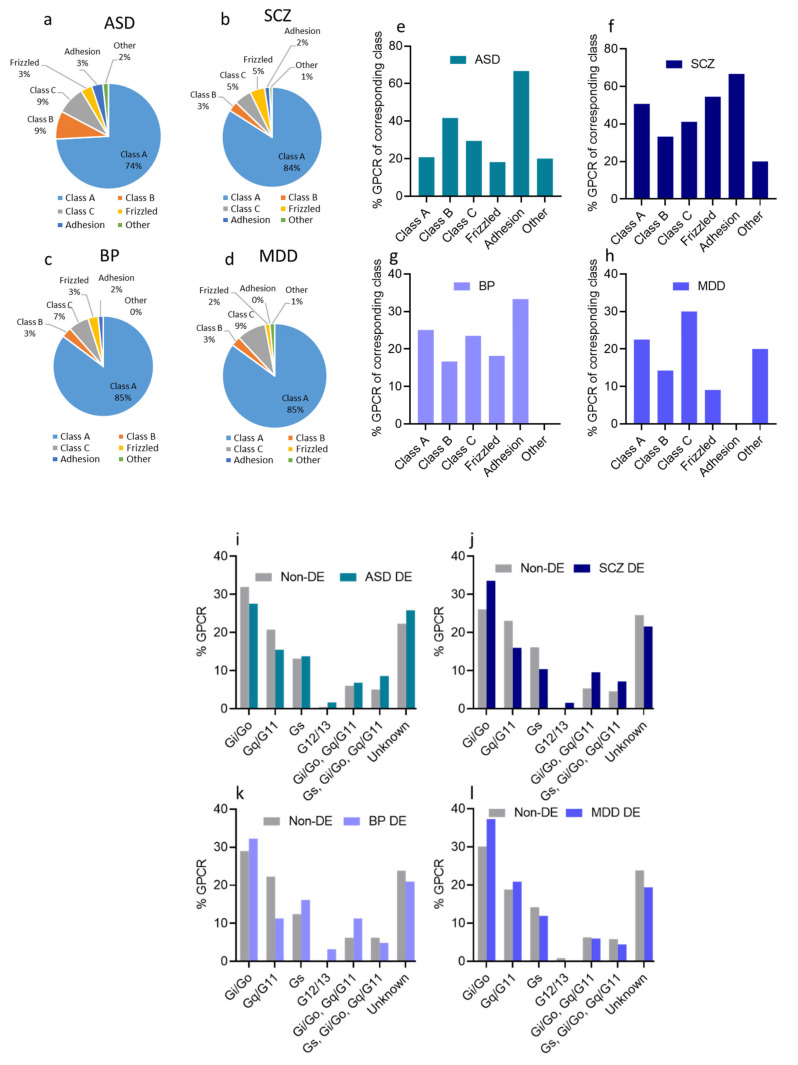
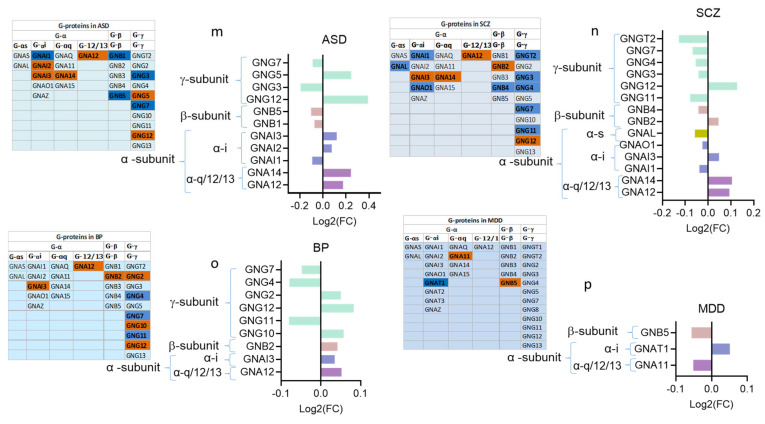
Figure 3.
Dysregulated GPCRs in psychiatric disorders belong to specific receptor subfamilies and couple to specific G-proteins; (a–d) Pie chart showing the distribution of DEs belonging to different GPCR sub-families as proportions of their corresponding total GPCR DEs in (a) ASD, (b) SCZ, (c) BP, and (d) MDD. (e–h) Histogram of the distribution of DEs belonging to different GPCR sub-classes in (e) ASD, (f) SCZ (g) BP, and (h) MDD, as proportions of the total subfamily genes. (i–l). Histogram of the distribution of differentially expressed (DE) and non-DE GPCR genes frequencies to the different G-proteins in (i) ASD, (j) SCZ, (k) BP, and (l) MDD. (m–p) G-protein isoforms’ dysregulations in (m) ASD, (n) SCZ, (o) BP, and (p) MDD, (left panel): chart showing different G-protein isoforms of the three G-protein subunits, downregulated: blue, upregulated: red; (right panel): log2(FC) of differentially expressed G-protein isoforms.