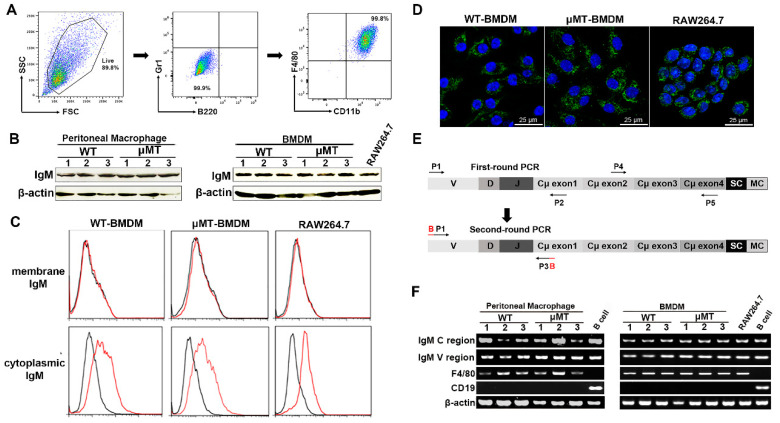
Figure 1.
IgM expression in primary macrophages in adult mice and RAW264.7 cell line. (A) Purity of the isolated CD11b+F4/80+ cells validated by flow cytometry. The representative flow cytometry analysis of in vitro differentiated BMDMs from WT and μMT mice demonstrate the purity of 99.9% and absence of B220+ B cells/Gr1+ granulocytes. (B) The mu heavy chain (IgM) was detected in peritoneal macrophages and BMDMs from WT and μMT mice and RAW264.7 cells by Western blot with goat anti-mouse IgM polyclonal antibody. β-actin acted as an internal control. (C) Flow cytometry analysis using AF488 labeled goat anti-mouse IgM mAb showed that IgM was localized only in the intracellular space of BMDMs from WT and μMT mice as well as RAW264.7 cells, but not on the plasma membrane of these cells. Black line, isotype control IgG1; red line, anti-mouse IgM. (D) Confocal microscopy analysis of BMDMs from WT and μMT mice and RAW264.7 cells using goat anti-mouse IgM polyclonal antibody showed that IgM was present in the intracellular space. DAPI (blue) was used for nuclear staining. Scale bars, 25 μm. (E) Diagrams (not to scale) of amplified DNA segments of IgM gene variable region and constant region by semi-nested PCR. The arrows indicate the positions of the listed primers in Table 1 used for amplification of the segments. (F) IgM gene rearrangement and transcriptions in sorted peritoneal macrophages and BMDMs from WT and μMT mice and RAW264.7 cells were analyzed by RT-PCR. The sorted CD19+ B cells were used as the positive control. F4/80 as macrophages-specific marker and CD19 as B cells markers were amplified. B, barcodes for primers to differentiate various samples in the next-generation sequencing; MC, membrane component; SC, secreted component; and β-actin as an internal control.