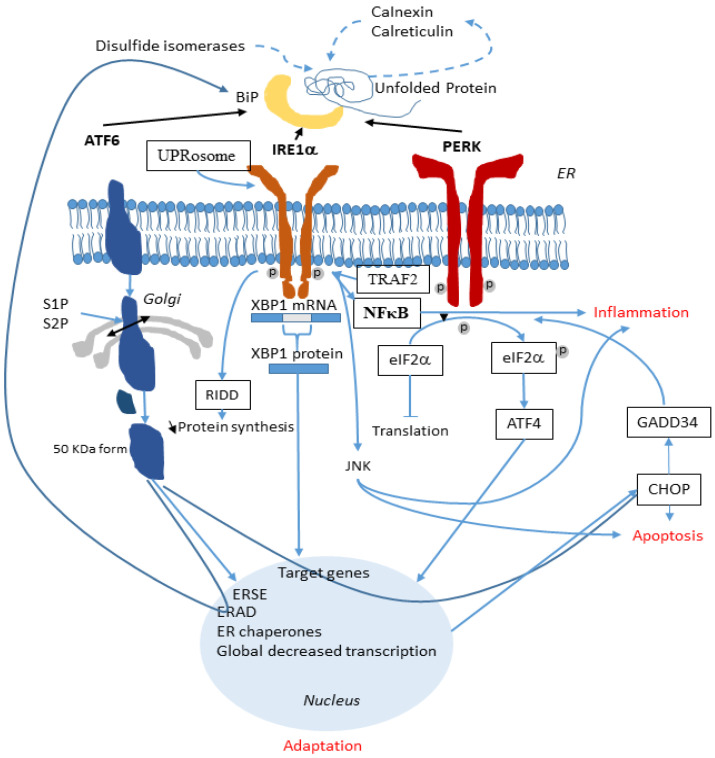
Figure 2.
Involvement of the UPR in the inflammatory response. In the ER, when ATF6, IRE1α and PERK are released from BiP, they activate the UPR (black lines). ATF6 is cleaved by S1P and S2P and its active form migrates to the nucleus. IRE1α splices XBP1 mRNA and the XBP1 protein is translocated to the nucleus. PERK phosphorylates eIF2α which also reach the nucleus. These three arms of the UPR activate specific genes aimed at alleviating the ER stress. During this process, inflammation is triggered (blue lines). A synergistic effect of both IRE1α and PERK permits the complete NF-κB activation through an interaction between IRE1α and TRAF2 and through the JNK pathway. UPR also activates the release of the pro-inflammatory IL-6 and IL-8. NF-κB is the main link between UPR and inflammation.