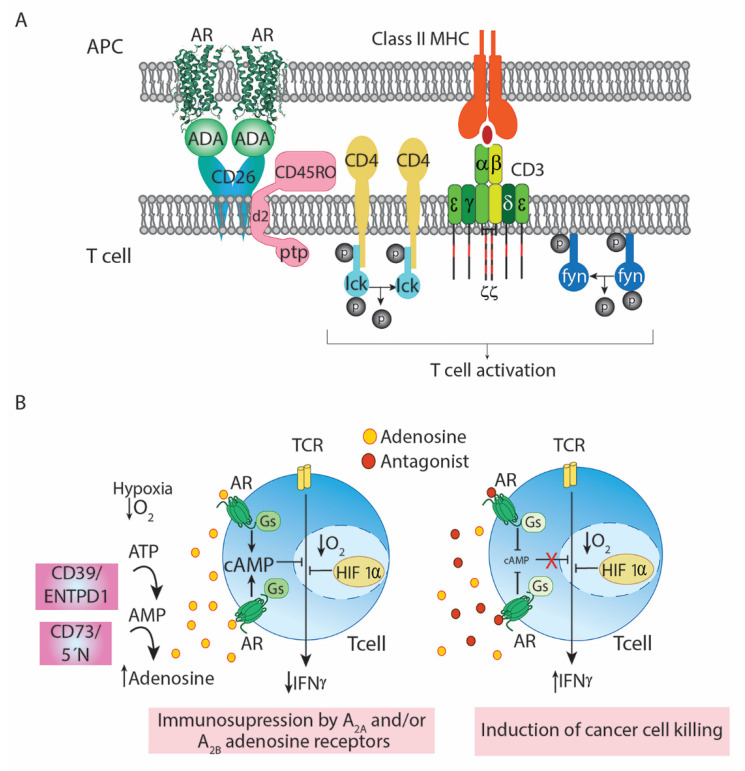
Figure 1.
Immunosuppressive actions of Ado in tumor microenvironment and rescue by AR antagonists. Panel (A) Proposed model of the CD26/Ado deaminase/AR-mediated co-stimulation of T-cells upon antigen presentation. Protein Src kinases such as Lck (which constitutively binds to the cytosolic domain of T-cell coreceptors CD4 or CD8) and Fyn are activated following TCR/CD3/CD4 cross-linking on T-cell surface promoted by the interaction of Major Histocompatibility Complex (MHC) proteins with antigens in presenting cells. These Src kinases phosphorylate immunoreceptor tyrosine-based activation motif (ITAM) in the cytosolic region of CD3γ, CD3δ, CD3ε, and CD3ζ (red lines). Phosphorylation allows recruitment of other protein tyrosine kinases to the ITAM on CD3ζ, which is phosphorylated and activated by Lck. These other kinases will activate intracellular signaling pathways leading to T-cell activation. In parallel, ADA1 adenosine deaminase anchored to the A2B AR on the antigen-presenting cell surface bridges the T-cell via cell surface CD26, at the same time that antigen is sensed by the T-cell receptor/CD3 complex. Subsequent to T-cell activation, CD45RO phosphatase bound to CD2, (via the d2 intracellular domain) is activated and recruited to the lipid rafts. The protein Tyr phosphatase (ptp) domain of CD45RO catalyzes the dephosphorylation of the regulatory domain of Src kinases including Lck and Fyn, thus inducing Src kinase activation. The model shown is similar for CD4+ T cells and CD8+ T cells. Abbreviations: d2, intracellular domain d2 of CD45RO; ptp, tyrosine-phosphatase domain of CD45RO. Adapted with permission from ref. [48]. 2007 Copyright Begell House Inc. Panel (B) Mechanism by which antagonists of Gs-coupled ARs rescue the anti-tumor activity of effector T cells. Elevated extracellular (Ado) in the tumor environment leads to immunosuppression. The hypoxia-induced increase in the expression of two ecto-nucleotidases, CD39 (ecto-nucleotide tri(di)phosphohydrolase-1 -ENTPD1-) and CD73 (5′-nucleotidase -5′N-)) in the tumor microenvironment results in enhanced conversion of extracellular adenine nucleotides into extracellular Ado. Activation of ARs leads to increases in cAMP, thus leading to impaired function of the effector cells of the immune system. Hypoxia also stabilizes the transcription factor HIF-1a, which cooperates with the ARs to suppress T-cell effector functions (left). Blockade of Gs-coupled ARs (A2AR and A2BR) restores the levels of intracellular cAMP, rescues the immunosuppression and enhances cancer cell killing by effector cells (right). Adapted from ref. [63].