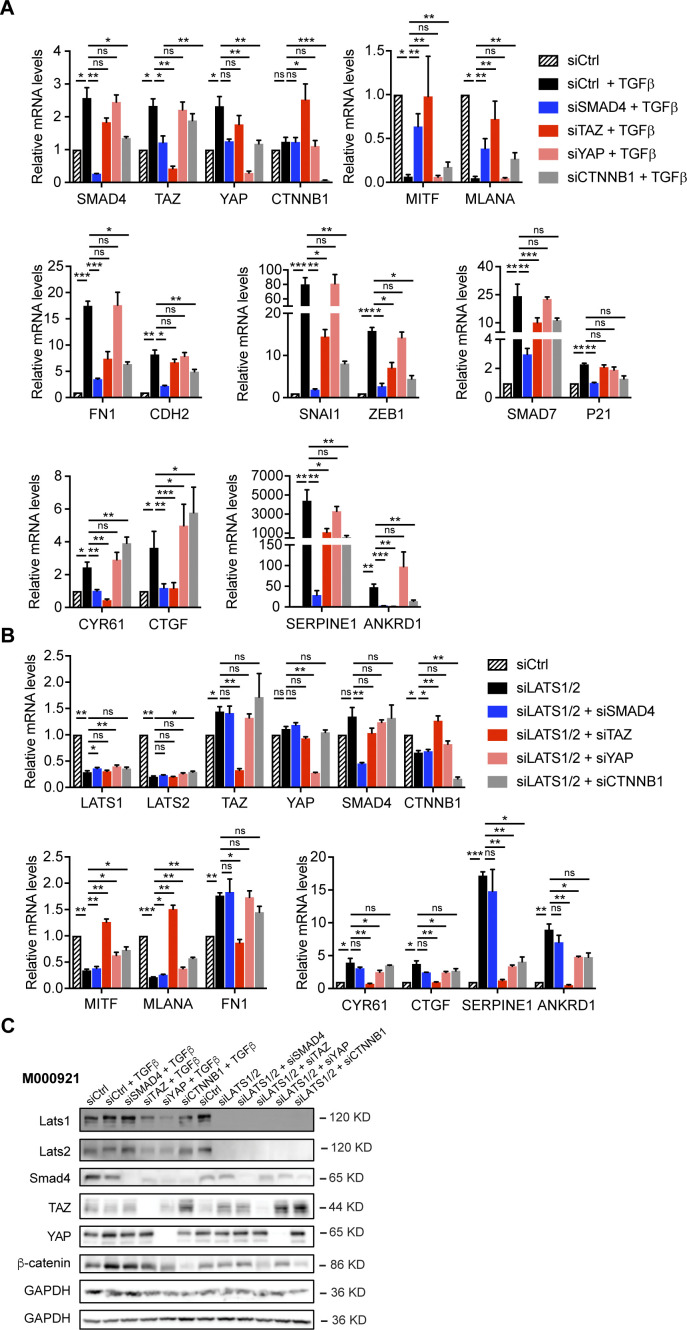
Figure S5. SMAD4, TAZ, and β-catenin are required for a proliferative-to-invasive phenotype switch in M010817 cells.
(A) Quantitative RT-PCR analysis to assess knockdown efficiencies as well as expression of melanocyte marker genes (MITF and MLANA), mesenchymal marker genes (FN1 and CDH2), epithelial–mesenchymal transition transcription factors (SNAI1 and ZEB1) and SMAD (SMAD7 and P21), YAP/TAZ (CYR61 and CTGF), and SMAD/YAP/TAZ target genes (SERPINE1 and ANKRD1) upon knockdown of SMAD4, TAZ, YAP, and β-catenin (CTNNB1) after 2 d of an TGFβ-induced phenotype switch. (B) Quantitative RT-PCR analysis to assess knockdown efficiencies as well as expression of melanocyte marker genes (MITF and MLANA), mesenchymal marker genes (FN1), and YAP/TAZ target genes (CYR61, CTGF, SERPINE1, and ANKRD1) upon knockdown of SMAD4, TAZ, YAP, and β-catenin (CTNNB1) during 2 d of an siLATS1/2-induced phenotype switch. Mean + SEM of n = 3 replicates are shown. *P < 0.05; **P < 0.01; ***P < 0.001; ratio-paired t test. (A, B, C) The knockdown efficiencies in the cells treated with the various siRNAs as described in panels (A) and (B) was assessed by immunoblotting with antibodies against the proteins indicated.