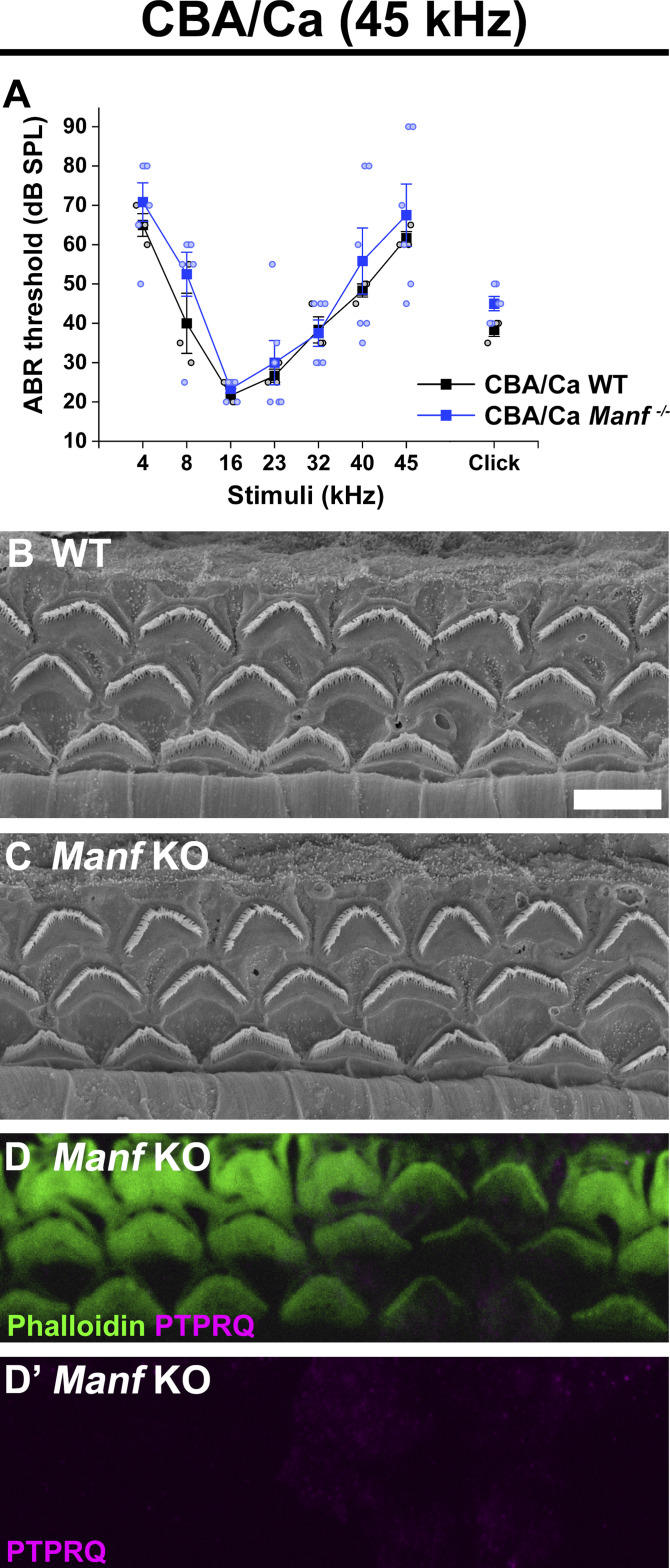
Figure 7. The strain-dependent genetic background dictates the phenotype of Manf-inactivated outer hair cells (OHCs).
(A) ABR thresholds between Manf KO and wild type mice under CBA background are without significant differences throughout the frequency region (4–45 kHz), analysed at P56 (compare to age-matched Manf cKO B6 mice, Fig 1E). One-way ANOVA P-values: tone stimuli 4 kHz P = 0.458, 8 kHz P = 0.234, 16 kHz P = 0.407, 23 kHz P = 0.700, 32 kHz P = 0.881, 40 kHz P = 0.563, 45 kHz P = 0.632; click stimulus: P = 0.054. Animals per group: Manf KO CBA n = 6, wild-type CBA n = 3. Error bars show ± SE. (B, C) SEM images from the 45 kHz region of cochleas of WT and KO CBA mice show a comparable OHC hair bundle phenotype. (D) PTPRQ immunostaining coupled with phalloidin labeling shows the absence of PTPRQ expression in the 45-kHz OHC hair bundles in Manf KO CBA mice, consistent with the normal bundle morphology (compared to age-matched Manf cKO B6 mice, Fig 5A–D′). Abbreviations: ABR, auditory brainstem response; B6, C57BL/6J strain; CBA, CBA/Ca strain; cKO, conditional knock out; KO and Manf−/−, knock out; OHC, outer hair cell; PTPRQ, protein tyrosine phosphatase receptor type Q; SE, standard error of the mean; SEM, scanning electron microscopy; SPL, sound pressure level; WT, wild type. Scale bar: (B) 5 μm in all images.