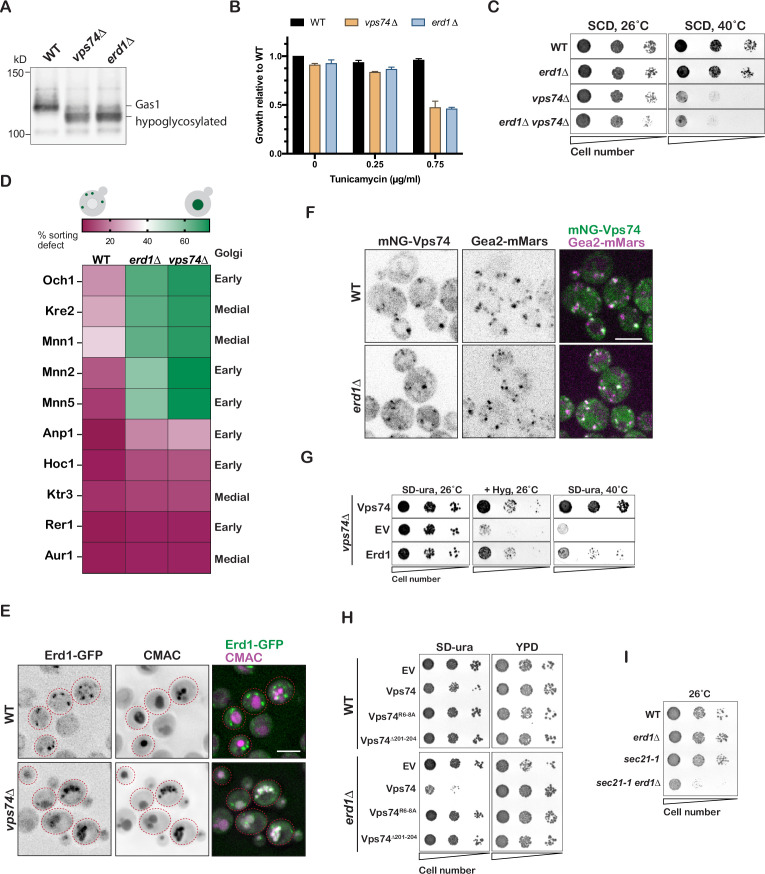
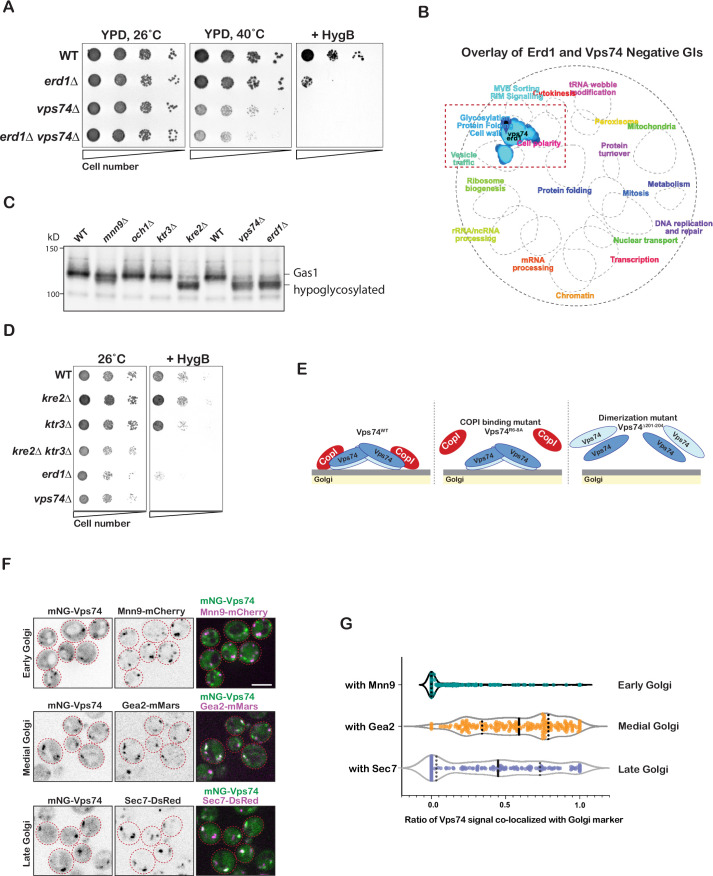
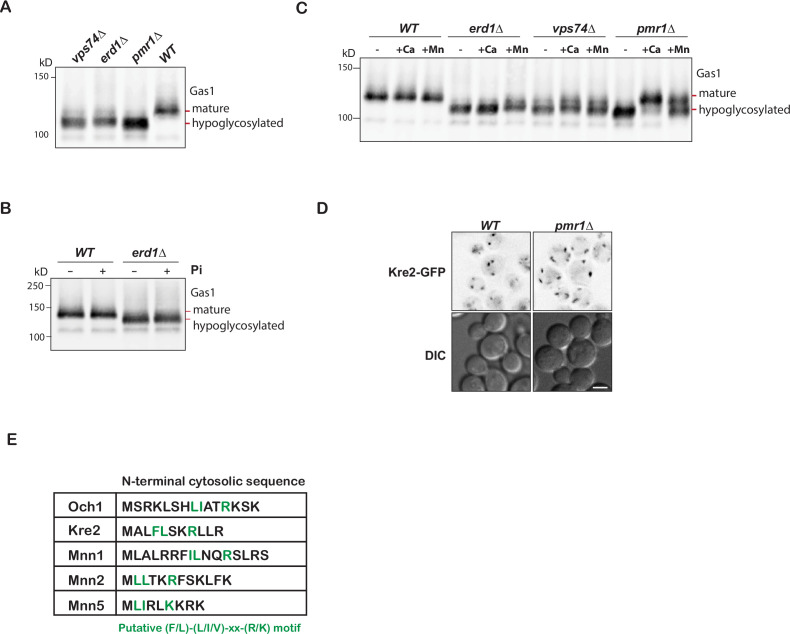
Figure 2. Erd1 is required for Vps74-COPI dependent recycling of specific Golgi glycosyltransferases.
(A) Immunoblot analysis on yeast cell lysates from wild type, erd1, and vps74 mutant for glycosylation reporter, Gas1. (B) Growth of wild type, erd1, and vps74 mutant in the presence of indicated concentrations of Tunicamycin in YPD liquid cultures at 30° C after 24 hr. (C) Growth of serial dilutions of wild type, erd1, vps74, and erd1vps74 mutants on synthetic media at 26 °C and 40° C after 2 days. (D) Quantification of percent vacuolar fluorescence to total fluorescence of the indicated GFP tagged early and medial Golgi proteins in wild type, erd1, and vps74 mutant. (E) Live-cell fluorescence imaging of Erd1-GFP and vacuolar dye, CMAC in wild type and the vps74 mutant. (F) Live-cell fluorescence imaging of mNeonGreen-Vps74 and medial Golgi marker, Gea2-3xMars in wild type and the erd1 mutant. (G) Growth of serial dilutions of vps74 mutant transformed with empty vector (EV) or plasmids overexpressing Vps74 and Erd1 on YPD with 50 µg/ml hygromycinB at 26 °C or synthetic media lacking uracil at 26 °C or 40° C after 2–3 days. (H) Growth of serial dilutions of wild type and erd1 mutant transformed with the indicated Vps74 mutants at 26° C after 3 days. (I) Growth of serial dilutions of wild type, erd1, sec21-1, and sec21-1 erd1 mutants at 26 °C after 3 days. Scale bars: 2.5µ m.