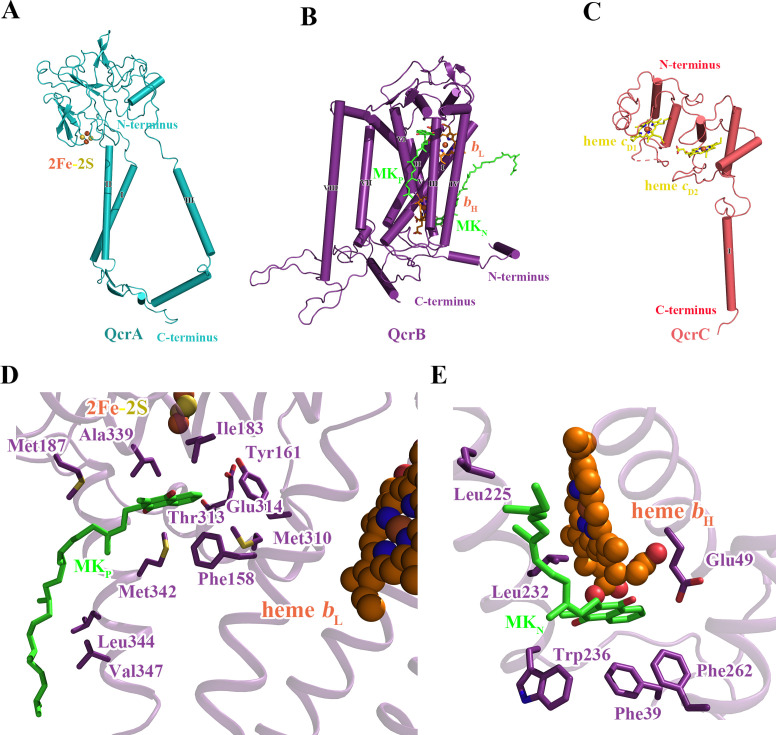
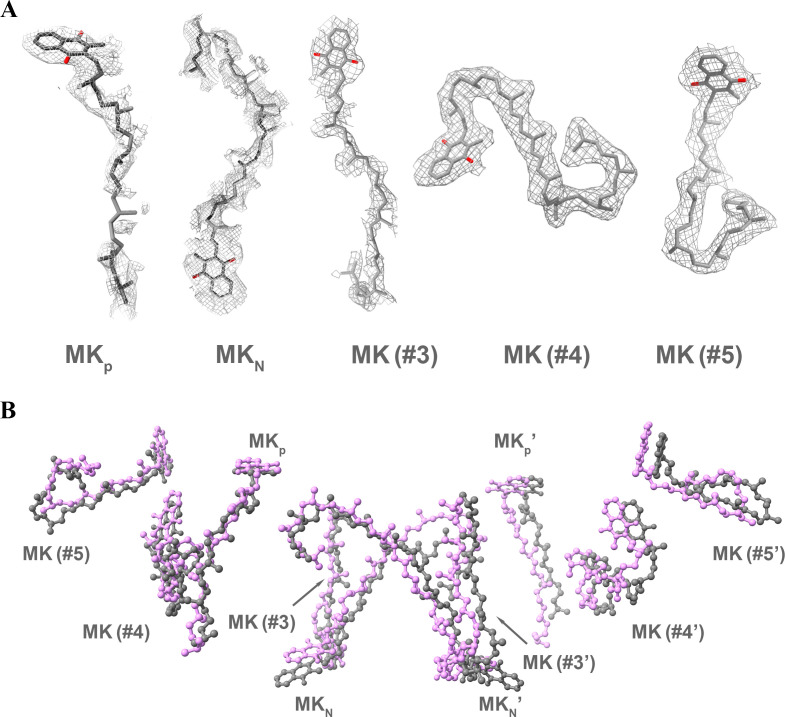
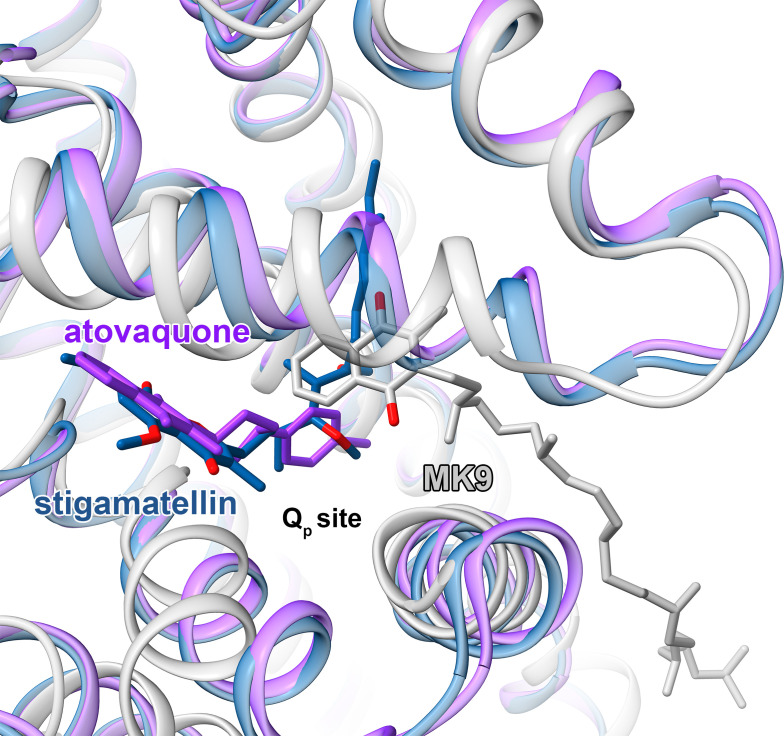
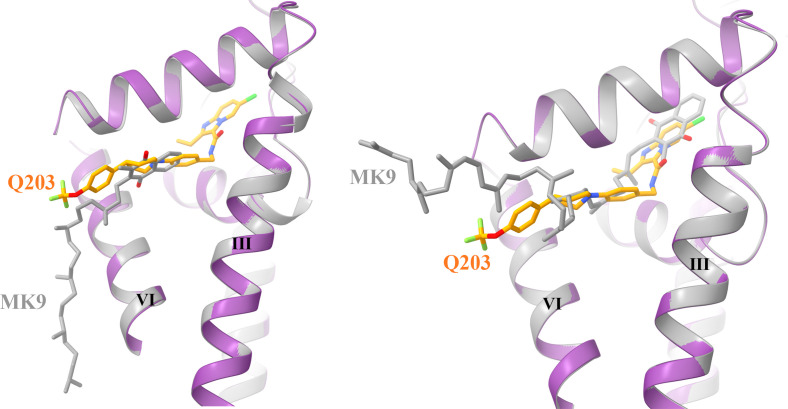
Figure 3. Structure of the M. tuberculosis cytochrome bcc subunits.
Cartoon representation of the monomers of (A) QcrA, (B) QcrB, and (C) QcrC, with prosthetic groups. (D) The QP-binding site and (E) QN-binding site. The residues potentially involved in the binding of MK/MKH2 are shown with side chains in stick model representation. MK/MKH2 have their carbon atoms in green and are represented as stick models. The [2Fe-2S] and heme groups are shown as spheres and labeled.