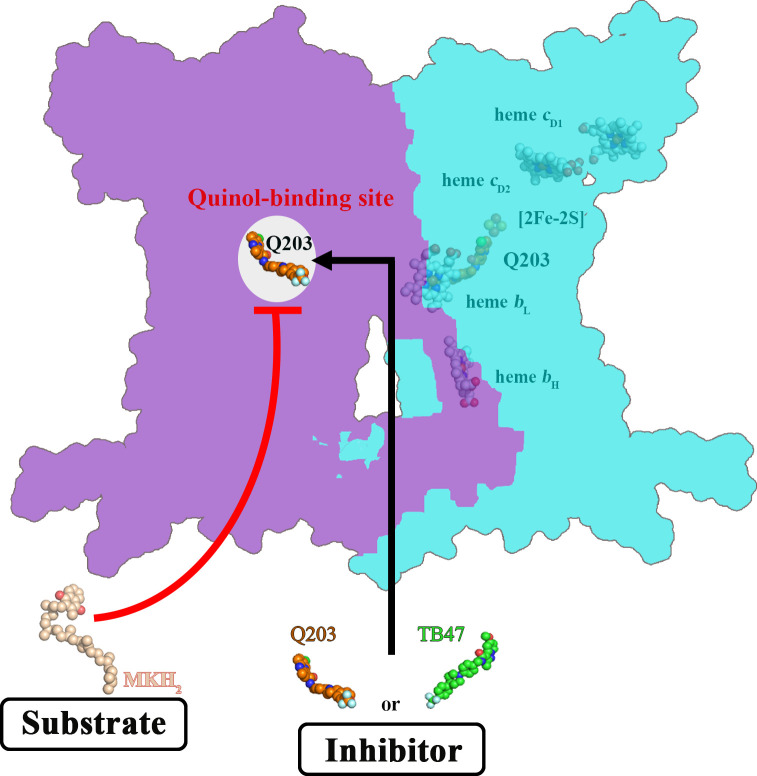
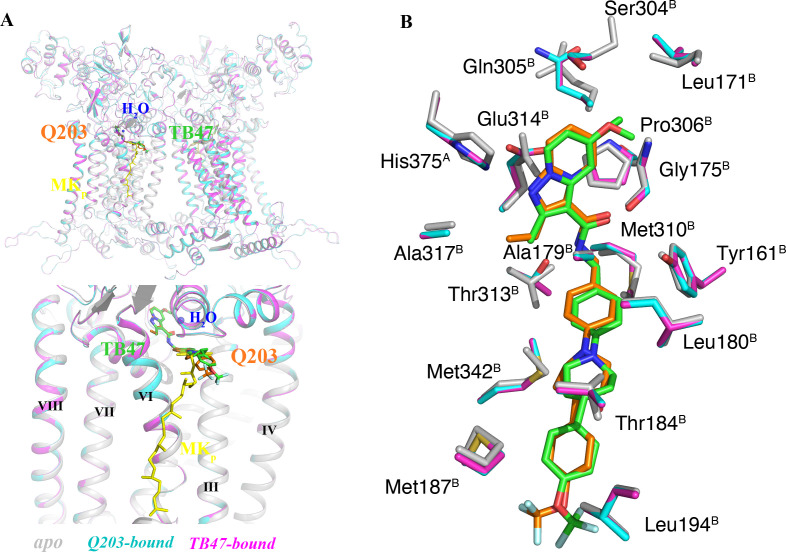
Figure 7. Schematic of M. tuberculosis cytochrome bcc inhibition by Q203 and TB47.
The two monomers of M. tuberculosis cytochrome bcc are colored magenta and cyan, respectively. The binding of Q203 (orange spheres) or TB47 (green spheres) prevents substrate access (gray spheres).