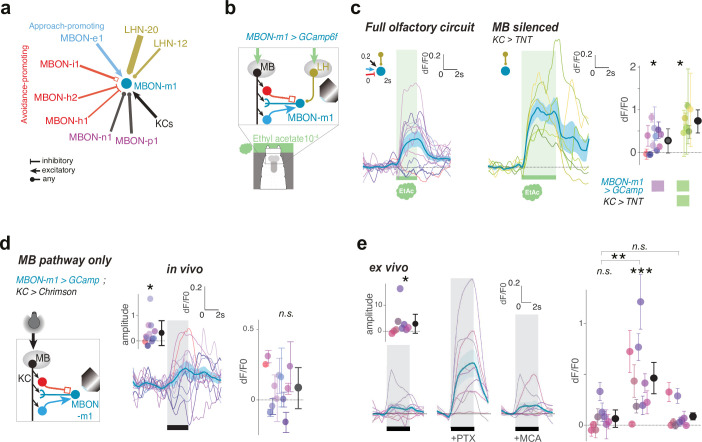
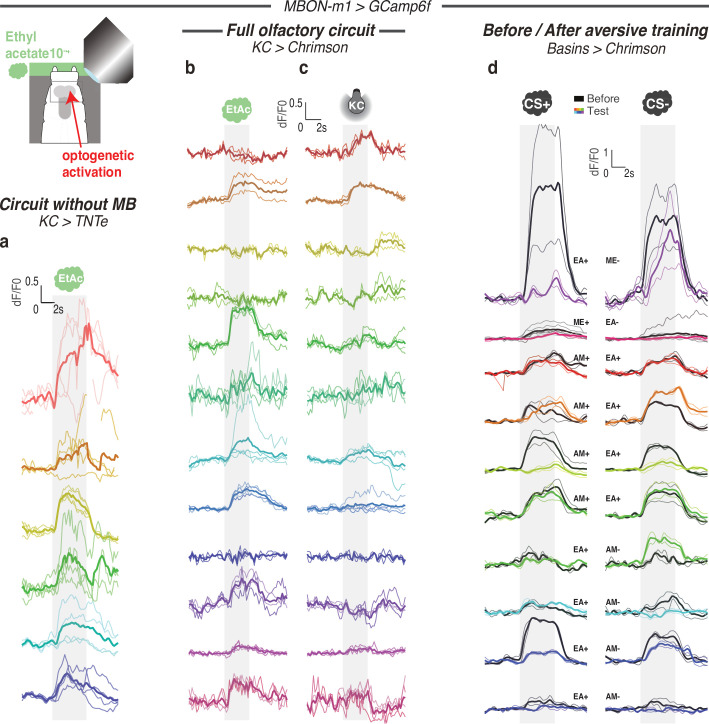
Figure 4. MBON-m1 receives functional inputs from LH and MB.
(a) MBON and LHN inputs onto MBON-m1 revealed by EM reconstruction. (b) Calcium activity of MBON-m1 in response to an innately attractive odor (EA) (c) and/or to optogenetic activation of CsChrimson-expressing KCs (d) was imaged in vivo in first instar larvae immobilised in a microfluidic chip as in Si et al., 2019. (c–e) Plots show fluorescence normalized to baseline (prior to odor presentation, δF/F0). Scores are calculated for the first 3 s of odor presentation. *: p < 0.05, **: p < 0.01, ***: p < 0.001, Wilcoxon test. See Figure 4—figure supplement 2 for individual animal responses. (c) Left, In untrained larvae MBON-m1 is excited by the innately attractive odor (N = 12). Middle, Silencing the MB pathway (by expressing TNTe in KCs) does not impair the excitatory response of MBON-m1 to the innately attractive odor (N = 6). This confirms a functionally excitatory connection from LHNs to MBON-m1. Right, quantification shows significant MBON-m1 responses to odor in the presence (left) and absence (middle) of a functional MB pathway. The comparison suggests that in the naive animals the excitatory odor drive could come mainly from the LH pathway. (d) Across the population of untrained larvae, the average change in δF/F0 in response to optogenetic activation of KCs is not significantly different from 0. However, the amplitude of δF/F0 (|max δF/F0 - min δF/F0|) was significantly increased after, compared to before, KC activation, suggesting that MBON-m1 receives functionally excitatory inputs from the MB in some individuals, and inhibitory in others (N = 12). (e) Activation of KCs in brain explants together with pharmacological blockers confirm mixed inhibitory and excitatory inputs from the MB pathway (N = 9). In saline, MBON-m1 response to KC activation does not differ from zero, with excitatory or inhibitory responses depending on individuals (inset shows the amplitudes of the responses significantly differ from zero). However, when bathed with PTX, thereby blocking chloride gating GABA and glutamate receptors, MBON-m1 is robustly excited by KC activation. Bath with MCA mostly abolishes the response to KC activation.