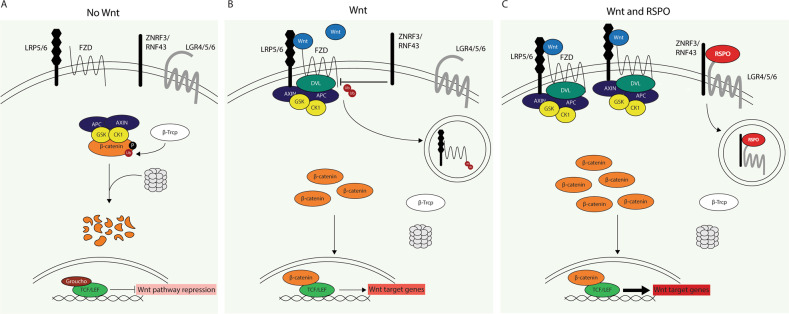
Fig. 1. The canonical Wnt pathway and the potentiating effect of RSPO.
A In the absence of canonical Wnt ligands the central destruction complex induces β-catenin degradation, restraining the transcription of Wnt target genes. B Canonical Wnt ligands induce dissociation of β-catenin from the degradation complex, leading to β-catenin accumulation, nuclear translocation and transcription of Wnt target genes. Ubiquitin ligases ZNRF3/RNF43 negatively regulate the Wnt pathway by internalizing and degrading membrane receptors LRP5/6 and FZD, thereby reducing Wnt receptor availability at the membrane. C RSPOs potentiate the canonical Wnt pathway by clearing negative regulators ZNRF3/RNF43 from the membrane, thereby increasing membranous Wnt receptor availability and potentiation of Wnt ligand-mediated pathway activation.