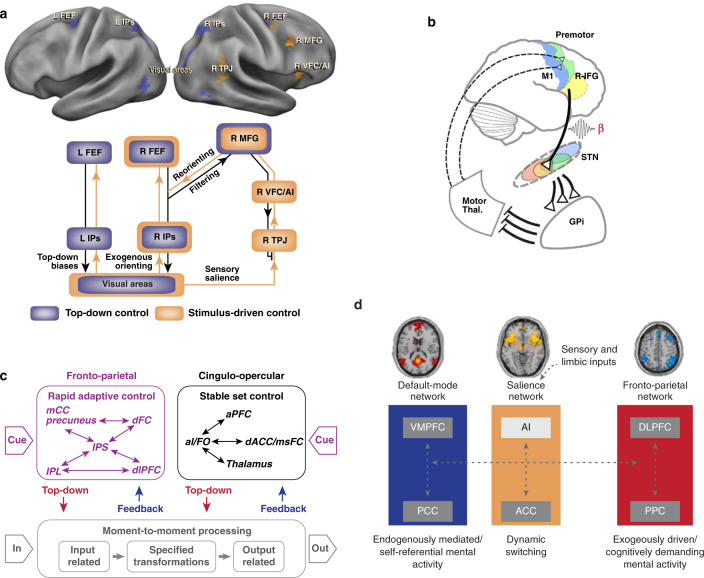
Fig. 4. Dynamic mechanisms of PFC network function.
a A circuit breaker for spatial attention. The VAN is hypothesized to act as a “circuit breaker” on the DAN, directing attention to salient events. Adapted from [32]. b Hypothetical model of different hyperdirect cortico-STN pathways for stopping and conflict processing. A, Stopping is initiated via right inferior frontal gyrus (R-IFG) in concert with the pre-SMA and implemented via projections to the subthalamic nucleus (STN) adapted from [157]. c Dual-network model of cognitive control which comprises parallel rapid-adaptive (FPN) and set-maintenance (CON) networks. Thin arrows schematize strong functional connections and boxed arrows schematize putative flow of information. The CON is hypothesized to maintain task-sets while the FPN rapidly adjusts adaptive control. Adapted from [62]. d Network switching model in which the SN is hypothesized to initiate dynamic switching between the FPN and DMN and regulate attention to endogenous and exogenous events. Sensory and limbic inputs are processed by the anterior insula (AI), which detects salient events and initiates appropriate control signals for (i) access to resources for working memory in FPN and (ii) action selection via the anterior cingulate cortex. Adapted from [8, 93].