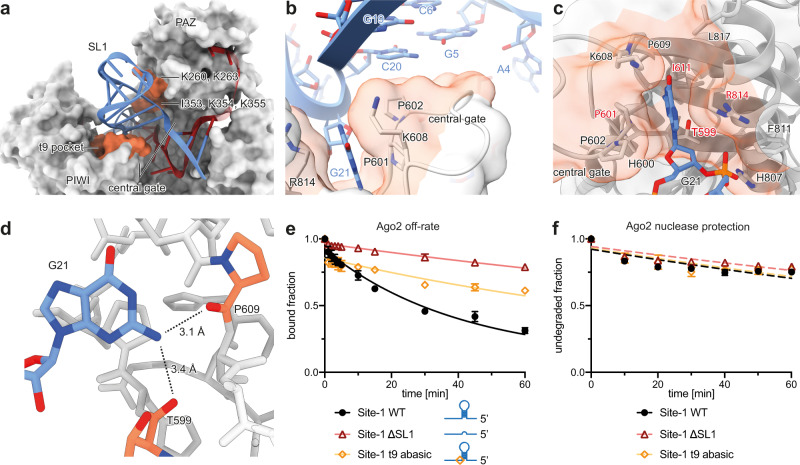
Fig. 3. SL1 and G21/t9 hold Ago2 in an open conformation.
a Detailed interactions between Ago2 and SL1. SL1 inserts between the PAZ and PIWI domains, on top of the PIWI loop of the central gate, a structure that antagonizes continuous base pairing to the miRNA central region. Ago2 surface contacting the viral RNA is shaded in orange. The interface with the PAZ domain is formed by two rows of residues. b Close up view showing the PIWI domain central gate loop inserts under SL1. Note this loop also contributes to the G21/t9 binding pocket. Ago2 surface contacting the viral RNA is shaded in orange. c Close up of PIWI domain G21/t9-binding pocket, shown with Ago2 in cartoon representation with transparent surface, and interface residues as sticks. Main contributors to the nucleobase interface labeled in red. Ago2 surface contacting the viral RNA is shaded in orange. d Side view of G21 in the hydrophobic pocket. Functional groups within H-bond distance of the 2-amino moiety indicated by dashes. e Release of Site-1 WT, Site-1 ∆SL1, and Site-1 t9 abasic from Ago2:miR-122 over time. Data shown as means of 3 independent replicates with error bars representing SEM. f Degradation of Ago2:miR-122 bound Site-1 WT, Site-1 ∆SL1, and Site-1 t9 abasic over time in presence of XRN1. Data shown as means of 3 independent replicates with error bars representing SEM.