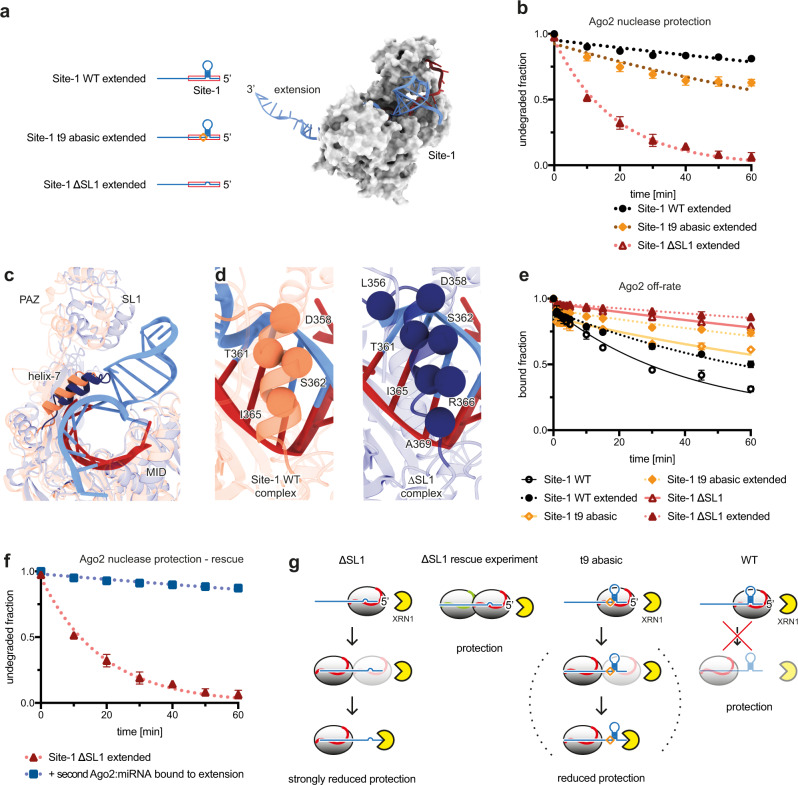
Fig. 4. SL1 protects from XRN1 by attenuating Ago2 lateral diffusion.
a Cartoons of extended Site-1 WT, ∆SL1 and t9 abasic RNA constructs (blue). Red box indicates Site-1. Model of the extended Site-1 WT (blue ribbon) in complex with Ago2:miR-122, to illustrate the relative size of the 3’ extension. b XRN1 mediated degradation of 3’ extended Site-1 WT, t9 abasic, and ∆SL1 in the presence of Ago2:miR-122 over time. Data are shown as means of 3 independent replicates with error bars representing SEM. c PAZ domain and helix-7 positions (relative to MID-PIWI lobe) in structures of Ago2:miR-122 bound to HCV Site-1 (coral), or seed plus supplementary paired RNA (dark blue, PDB code 6N4O). d Comparison of the Ago2 helix-7-target RNA contacts (spheres centred at Cα atoms in contacting residues) for the Site-1, and seed plus supplementary paired RNA. The miRNA strand is coloured red and the target strand blue (only seed base pairs shown). e Release of Site-1 WT, ∆SL1, and t9 abasic Site-1 RNAs, with and without 3’ extensions, from Ago2:miR-122 over time. Data are shown as means of 3 independent replicates with error bars representing SEM. f XRN1 mediated degradation of extended Site-1 ∆SL1 RNA in presences of Ago2:miR-122-wt alone or in combination with Ago2:miR-122-mut (targeting the 3’ extension). Data are shown as means of 3 independent replicates with error bars representing SEM. g Cartoon representation of the proposed mechanism. Ago2:miR-122 transiently diffuses onto 3’ extensions in the absence of SL1, allowing XRN1 access to the HCV RNA 5’ end (left). The presence of a second Ago2:miRNA can prevent lateral diffusion, re-establishing protection (middle-left). Ago2:miR-122 also laterally diffuses from a Site-1 with a t9 abasic nucleotide, albeit at a reduced rate compared with the ∆SL1 construct, again enabling XRN1(middle-right). The full motif at Site-1 prevents Ago2:miR-122 lateral diffusion, and the target RNA is protected (right).