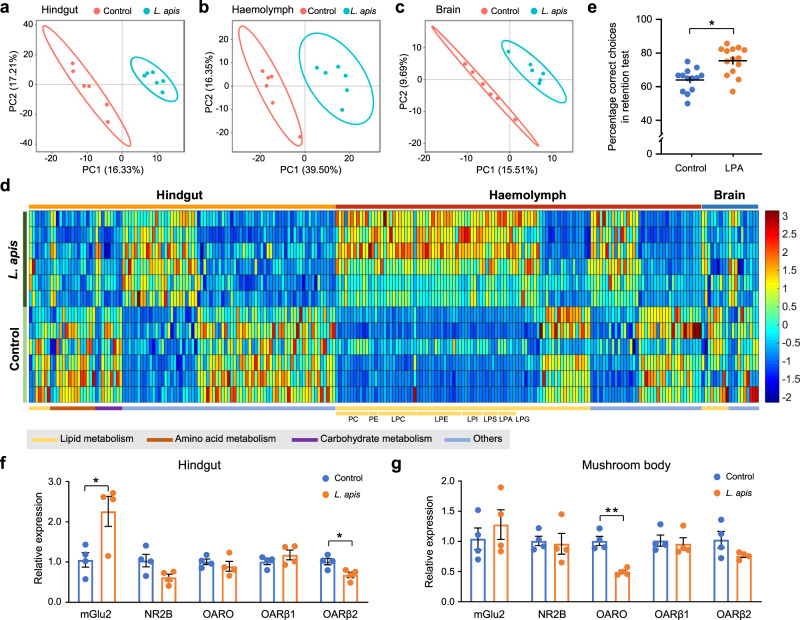
Fig. 3. L. apis supplementation affects host metabolites and neural receptor gene expressions in bees.
a–c Metabolomic analyses of bumblebee hindgut (a), haemolymph (b) and brain (c) samples from control and L. apis-fed bees. Partial least-squares discrimination analysis (PLS-DA) showed that the metabolomic profiles of the hindgut, haemolymph and brain in L. apis-fed and control bees differed (n = 6 for both groups). d Heatmap showing significantly altered metabolites in the bumblebee hindgut, haemolymph and brain. Colours indicate the normalised abundance of each metabolite. e The effect of one glycerophospholipid LPA (14:0) on long-term memory (GLMM, df = 24, p = 0.028; n = 13 for the Control group and n = 14 for the LPA group; Supplementary Table 3). f and g L. apis supplementation affects the gene expression of neural receptors in the host hindgut and brain mushroom body (two-sided Student’s t test: mGlu2 in the hindgut, t6 = 2.9175, p = 0.027; OARβ2 in the hindgut, t6 = −3.1301, p = 0.020; OARO in the mushroom body, t6 = −6.3565, p = 7.110 × 10−4; n = 4 bees for both groups). Asterisks indicate significant differences (*p < 0.05, **p < 0.01). Data are presented as mean ± SEM. PC phosphatidylcholine, PE phosphatidylethanolamine, LPC lysophosphatidylcholine, LPE lysophosphatidylethanolamine, LPI lysophosphatidylinositol, LPS lysophosphatidylserine, LPA lysophosphatidic acid, LPG lysophosphatidylglycerol, mGlu2 metabotropic glutamate receptor 2, NR2B glutamate receptor ionotropic NMDA 2B, OARO octopamine receptor Oamb, OARβ1 Octopamine receptor beta-1R, OARβ2 Octopamine receptor beta-2R. Source data are provided as a Source Data file.