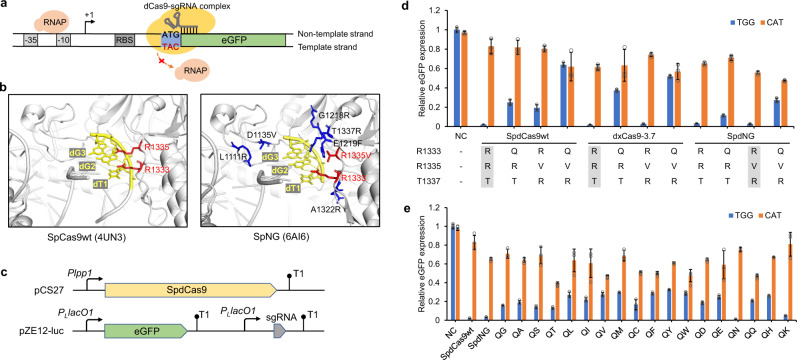
Fig. 1. Generation of dCas9 variants targeting 5′-CAT-3′ protospacer adjacent motif (PAM) sequence.
a Inhibition of transcription elongation from RNA polymerase (RNAP) when SpdCas9 variant was targeted to the start codon ATG of target genes. SpdCas9 variant recognizing 5′-CAT-3′ PAM sequence could bind at the start codon ATG, with sgRNA spacer complementary to the ATG adjacent sequence (20 bp) on the nontemplate DNA strand. The -35 and -10 boxes, and ribosome binding site (RBS), are shown in gray. +1, transcription initiation site. b PAM-interacting (red) or proximal residues (blue) in SpCas9wt (PDB ID: 4UN3) and SpNG (PDB ID: 6AI6). PAM sequence is shown in yellow. c The dual-plasmid eGFP repression system for SpdCas9 variant characterization: pCS27 containing Plpp1-controlled SpdCas9wt or variants and pZE12-luc containing PLlacO1-controlled eGFP and sgegfp-TGG or sgegfp-CAT. d Impact of mutating PAM interaction residues (R1333/R(V)1335/T(R)1337) in SpdCas9wt, dxCas9-3.7, and SpdNG on 5′-TGG-3′ (blue) and 5′-CAT-3′ (orange) PAM recognition. The residues in shaded boxes correspond to residues in unmutated SpdCas9wt, dxCas9-3.7, and SpdNG, respectively. e Impact of combinatorial mutations of R1333/V1335 in SpdNG on 5′-TGG-3′ (blue) and 5′-CAT-3′ (orange) PAM recognition. NC, E. coli BW25113(F′) cotransformed with the empty pCS27 plasmid and pZE-eGFP-sgegfp-TGG or pZE-eGFP-sgegfp-CAT. Data indicated the mean ± standard deviation (n = 3 independent biological replicates). Source data are provided as a Source Data file.