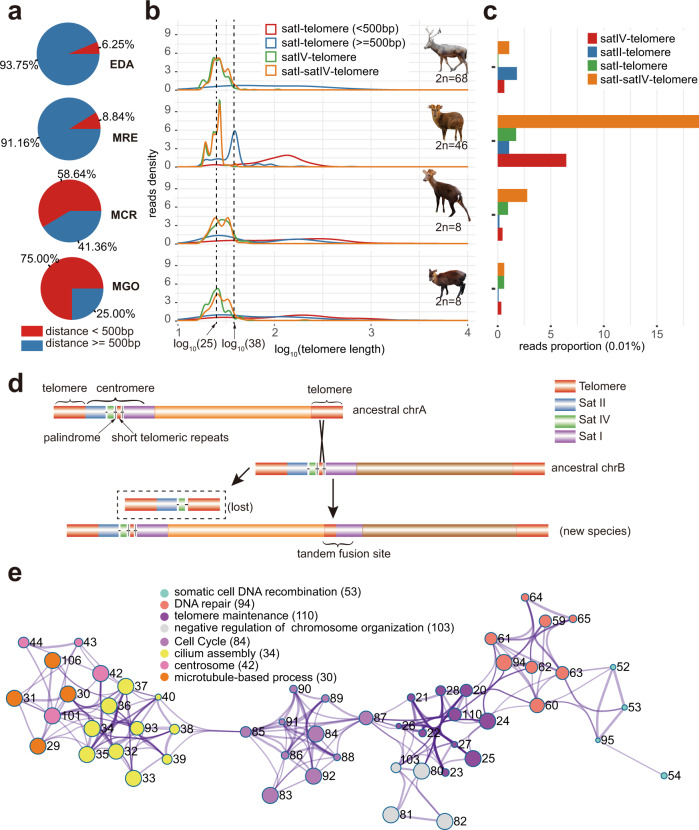
Fig. 3. Molecular basis of tandem chromosome fusion of muntjac species.
a Proportion of reads with distance between satellite I and telomeric repeats smaller (red) or longer (blue) than 500 bp. Only reads containing telomeric sequences and satellite I but not satellite II and IV are considered in this statistic. EDA, E. davidianus; MRE, M. reevesi; MCR, M. crinifrons; MGO, M. gongshanensis. b Kernel density estimate of reads with different length of telomeric sequence. Reads containing different combinations of satellite and telomeric sequence are displayed separately with colored lines. satI, satellite I; satIV, satellite IV; telomere, telomeric sequence. The top-to-bottom of species order is consistent with that of Fig. 3a. c Proportion of reads containing different combinations of satellite or telomeric repeats in all investigated reads of E. davidianus, M. reevesi, M. crinifrons, and M. gongshanensis. d Schematics of a conjectural mechanism of tandem fusion. DNA double-strand breaks occurred at palindromes nearby the short telomeric repeats, which mediated nonallelic homologous recombination between different ancestral muntjac chromosomes and led to the tandem fusions. e Network plot of GO terms enriched by REGs and PSGs of M. gongshanensis. REGs and PSGs are pooled in the GO enrichment analysis and each GO term is numbered. GO terms with a similarity >0.3 are connected by edges. Circles with the same color represent that GO terms belong to the same cluster. The size of each circle reflects the p value, where terms containing more genes tend to have a more significant p value. For each cluster, we display the name and number of a representative GO term. Only clusters related to cell cycle, nuclear division, DNA damage response or telomere maintenance are displayed here.