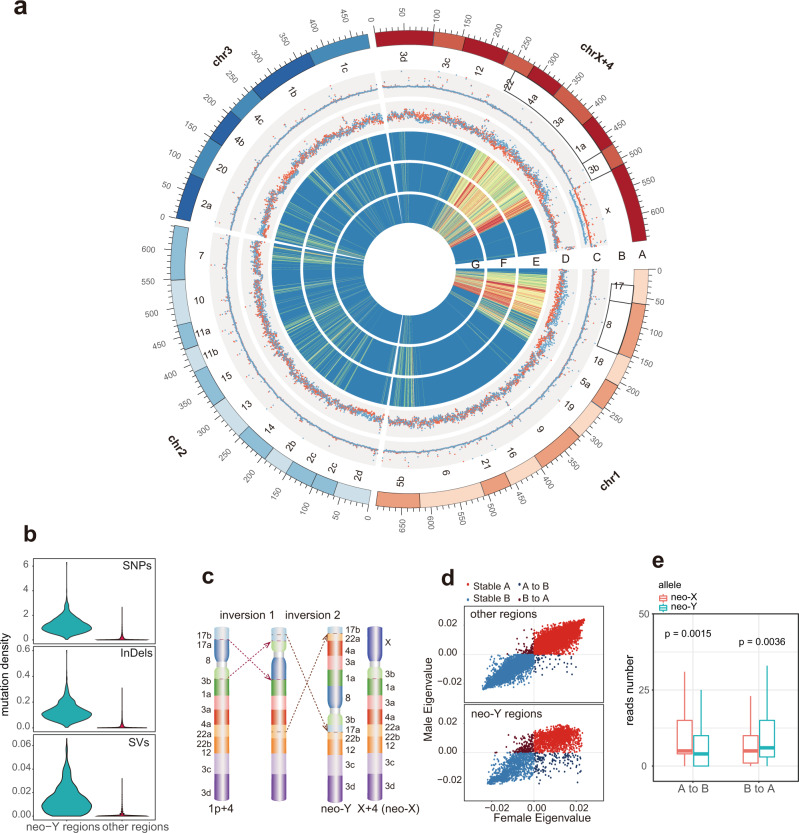
Fig. 4. Evolution of neo-sex chromosomes in M. crinifrons.
a Circos plot of female M. crinifrons genome. Track A: chromosomes of female M. crinifrons showed by 35 colored ancestral chromosomes. Track B: labels of ancestral chromosome under previous nomenclature21. Black frames enclose neo-X regions. Track C: Mapping coverage of female (red) and male (blue) M. crinifrons Illumina reads. Track D: SNPs and indels density of female (red) and male (blue) M. crinifrons. Track E: Heatmap showing the density of candidate male-specific SNPs. Density from low to high correspond the color group “spectral-7-div-rev” in circos. Track F: Heatmap showing the density of candidate male-specific indels with the same colors coding as track E. Track G: Heatmap showing the density of candidate male-specific SVs with the same colors coding as track E. b Violin plot showing the density of candidate male-specific mutations in neo-Y regions and other regions. c Two inversion events happened on the neo-Y chromosome of male M. crinifrons. Block 17a, 17b, 22a, and 22b are ancestral chromosomal segments disrupted by inversions and each of the remaining colored blocks represent the completed ancestral chromosome. d The eigen values of homologous bins in female and male M. crinifrons. Eigen value greater and less than zero means compartment A and B, respectively. The “other regions” indicate genomic regions excluding neo-Y regions and mammalian X chromosome region. e Boxplot of number of RNA-seq reads supporting neo-X or neo-Y allele in male M. crinifrons sample. “A to B” means compartment switch from A in neo-X regions of female M. crinifrons to B in homologous neo-Y regions of male M. crinifrons. “B to A” is opposite. There are 160 pairs of neo-X and neo-Y alleles in “A to B” regions and 366 pairs in “B to A” regions. The lower and upper hinges correspond to the first and third quartiles. The line inside box is the median. The whisker extends from the hinge to at most 1.5 * IQR (where IQR is distance between the first and third quartiles). Outliers are hidden. Difference in reads number supporting neo-X and neo-Y alleles was tested by two-sided Wilcoxon test (p value <0.05).