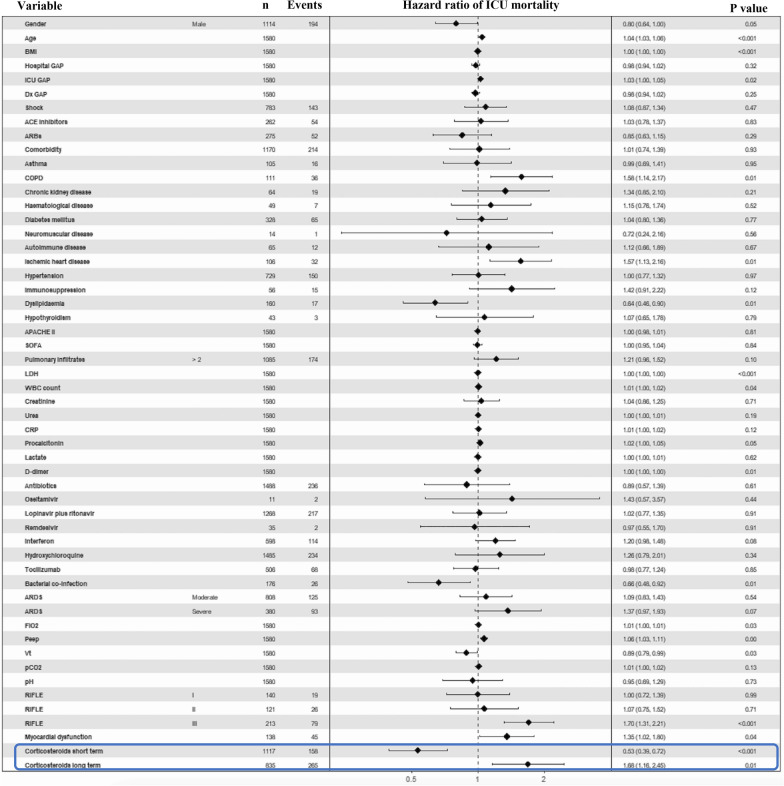
Fig. 2.
Forest plot of the cause-specific hazard model (time-dependent Cox regression) for ICU mortality. The time-dependent Cox regression included all the variables and those were adjusted as potential confounding factors. The interaction with time in this case was modelled using the step function to deal with non-proportional hazards of the covariate of interest (corticosteroid treatment). Through the step function, a partitioning of the time axis was made at day 17th, when the effect of the covariate changed over time. Consequently, the model allowed to estimate the effect of the treatment covariate before (corticosteroid treatment short-term) and after (corticosteroid treatment long-term) the 17th day of ICU admission. Notably, the regression model showed the protective effects of corticosteroids on survival up to day 17 of admission to the ICU, although these effects changed over time, as after the 17th day corticosteroid treatment at ICU admission was associated with higher mortality. Diagnosis GAP means the time (days) from disease onset to the confirmation of the diagnosis of SARS-CoV-2 infection; Hospital GAP (days) means the time from disease onset to hospital admission. ICU GAP (days) means the time from hospital to ICU admission. BMI body mass index, ACE angiotensin-converting enzyme, ARBs angiotensin receptor blockers, COPD chronic obstructive pulmonary disease, APACHE Acute Physiology And Chronic Health Evaluation, SOFA Sequential Organ Failure Assessment, LDH lactate dehydrogenase, WBC white blood cells count, CRP C-reactive protein, ARDS acute respiratory distress syndrome, FiO2 fraction of inspired oxygen, Peep positive end-expiratory pressure, Vt tidal volume, pCO2 partial pressure of carbon dioxide, RIFLE criteria Risk, Injury, Failure, Loss, End stage