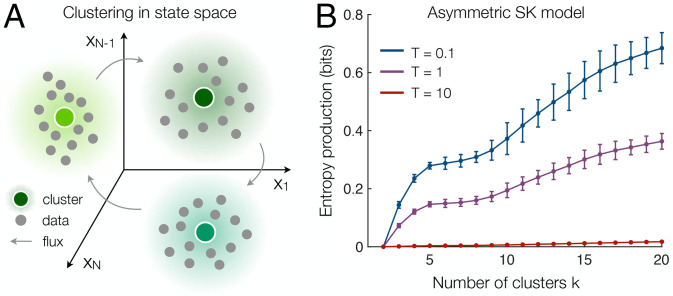
Fig. 3.
Estimating entropy production using hierarchical clustering. (A) Schematic of clustering procedure, where axes represent the activities of individual components (e.g., brain regions in the neuroimaging data or spins in the Ising model), points reflect individual states observed in the time series, shaded regions define clusters (or coarse-grained states), and arrows illustrate possible fluxes between clusters. (B) Entropy production in the asymmetric SK model as a function of the number of clusters k for the same time series studied in Fig. 2C, with error bars reflecting 2-SD confidence intervals that arise due to finite data (Materials and Methods).