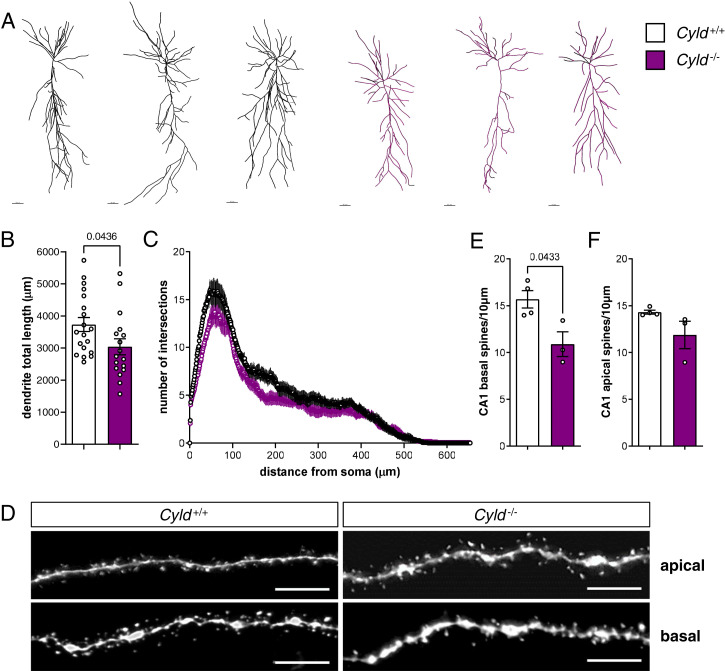
Fig. 4.
CYLD deletion results in reduced total dendrite length and basal spine number of CA1 hippocampal PNs. (A) Representative pictures of reconstructed biocytin-filled PNs by Imaris of Cyld−/− mice and Cyld+/+ controls at P42 in CA1. (B and C) Measurement of dendrite total length and Sholl analysis of CA1 PNs. (D) Representative pictures of apical and basal spines of Cyld−/− and Cyld+/+ PNs. (E and F) Quantification of basal and apical spines. For experiments in A through C, n = 19 neurons from Cyld+/+ controls and n = 17 neurons from Cyld−/− mice. For experiments in D through F, n = 4 for Cyld+/+ controls and n = 3 for Cyld−/− mice. The statistics were calculated by unpaired Student’s t test (B, E, and F) and two-way repeated ANOVA with Sidak’s (C) post hoc tests. Graphs are mean ± SEM. (Error bars in A: 40 µm; error bars in D: 5 µm.)