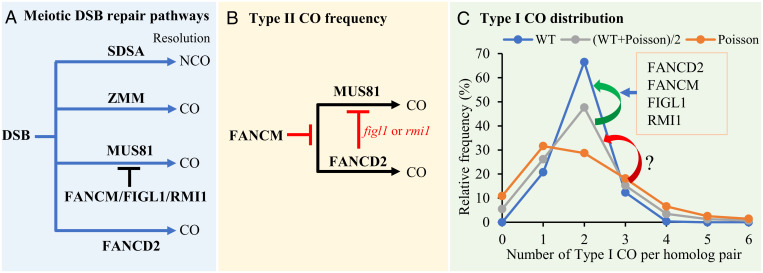
Fig. 5.
A proposed model for the regulation of CO frequency and distribution. (A) Meiotic DSBs can be repaired through synthesis-dependent strand annealing pathway as noncrossovers or ZMM pathway, as Type I CO or MUS81, and FANCD2 pathways as Type II CO, and FANCM, FIGL1, and RMI1 have distinct roles in limiting MUS81-dependent CO. (B) Besides limiting the formation of MUS81-dependent CO, our data show that AtFANCM also limits AtFANCD2-dependent CO and AtFANCD2 limits AtMUS81-dependent CO in Atfigl1 or Atrmi1 background. (C) The distribution of meiotic Class I COs among homologous chromosome pairs in WT plants (blue line) deviates significantly from a Poisson distribution (orange line) in which COs are positioned independently of one another. Based on our genetic analysis, the activities of AtFANCD2, AtFANCM, AtFIGL1, and AtRMI1 appear to control ∼50% of the difference between the WT and Poisson distributions. Mutations in any of these factors results in a distribution that is intermediate between WT and random Poisson (gray line). Factors that regulate the remaining 50% of the difference are yet to be determined. Arrowheads indicate the transition between different distribution patterns.