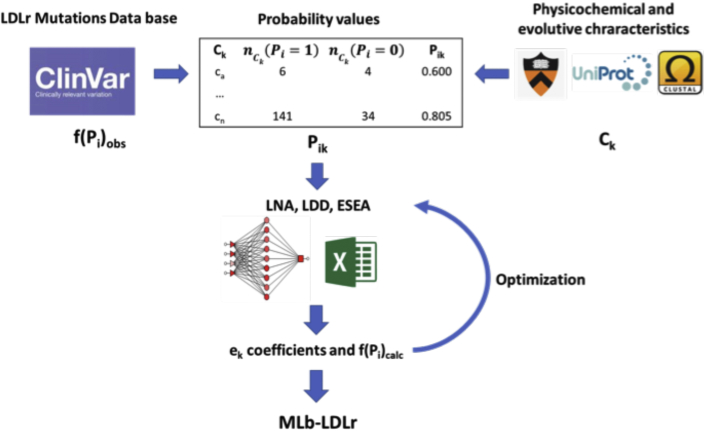
Figure 1.
General Workflow of the Model
Clinical significance of characterized LDLr variants (f(Pi)obs) and values of physicochemical and evolutive characteristics (Ck) were obtained from several software and databases. Pathogenicity probability values (Pik) were calculated using the relation between pathogenic and benign variants in each characteristic. Then, different ML models (LNN, LDA, ESEA) were applied to obtain the weight of each characteristic on the overall pathogenicity and the threshold that divides pathogenic and benign variants (ek coefficients). These values were later used to calculate a pathogenicity score of each variant (f(Pi)calc). Finally, some f(Pi)calc values were manually modified, and the ML models were applied again in order to optimize ek values. The resulting coefficients were used on MLb-LDLr software. ESEA = Excel Solver Evolutionary algorithm; LDA = linear discriminant analysis; LNN = linear neural network; ML = machine learning; MLb-LDLr = machine-learning–based low-density lipoprotein receptor software.