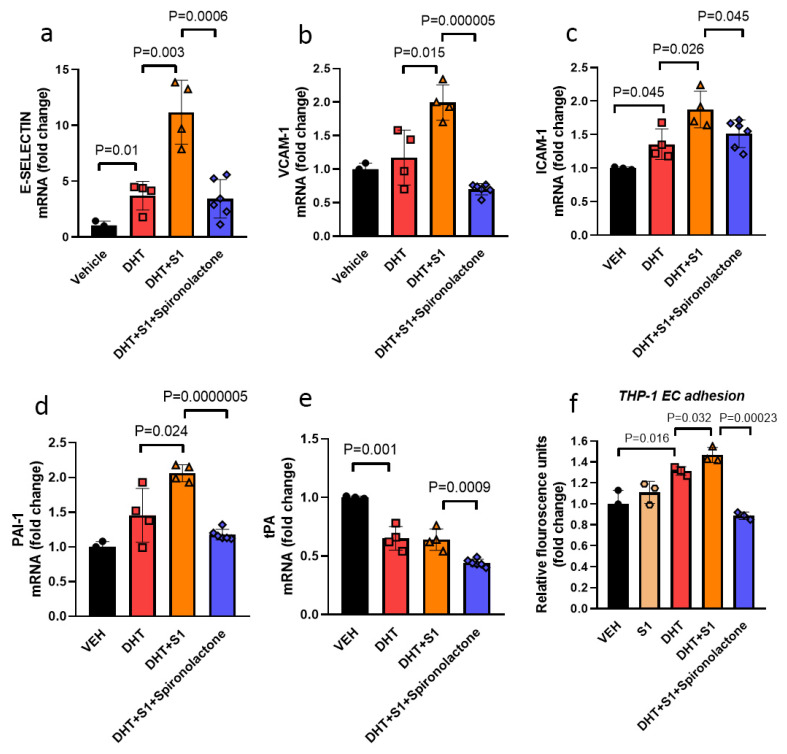
Figure 2.
Co-treatment of ECs with SARS-CoV2 S1 with dihydrotestosterone (DHT) in vitro enhanced gene expression of cell adhesion molecules and anti-fibrinolytic marker and promoted leukocyte adhesion, with beneficial effects of spironolactone treatment. (a) Transcript expression of cell adhesion molecule E-selectin was increased by DHT alone (500 nM) as compared to the vehicle and expression of E-selectin was enhanced by S1 (25 nM) in the presence of DHT (n = 4). (b,c) VCAM-1 and ICAM-1 transcript expression were also enhanced by S1 in the presence of DHT as compared to DHT alone. (d) Co-treatment of S1 with DHT enhanced PAI-1 transcript expression. (e) Transcript expression of fibrinolytic tPA was significantly downregulated by DHT alone, while co-treatment with S1 did not further change tPA transcript expression. (f) DHT treatment increased the adhesion of human THP-1 monocytes to EC monolayers, which was further enhanced by the S1 exposure. Spironolactone (10 mM) reduced the transcript expression of cell adhesion molecules (E-selectin, VCAM-1 and ICAM-1) and anti-fibrinolytic/fibrinolytic PAI-1/tPA, respectively, and blocked the adhesion of THP-1 to ECs monolayer in vitro (n = 3–4). ● (Vehicle), ■ (DHT), ▲ (DHT+S1), ♦ (DHT+S1+Spironolactone), ⬣ (S1). Data were analyzed by the analysis of variance (ANOVA). p < 0.05 was defined to be statistically significant. All data are expressed as mean ± s.d.