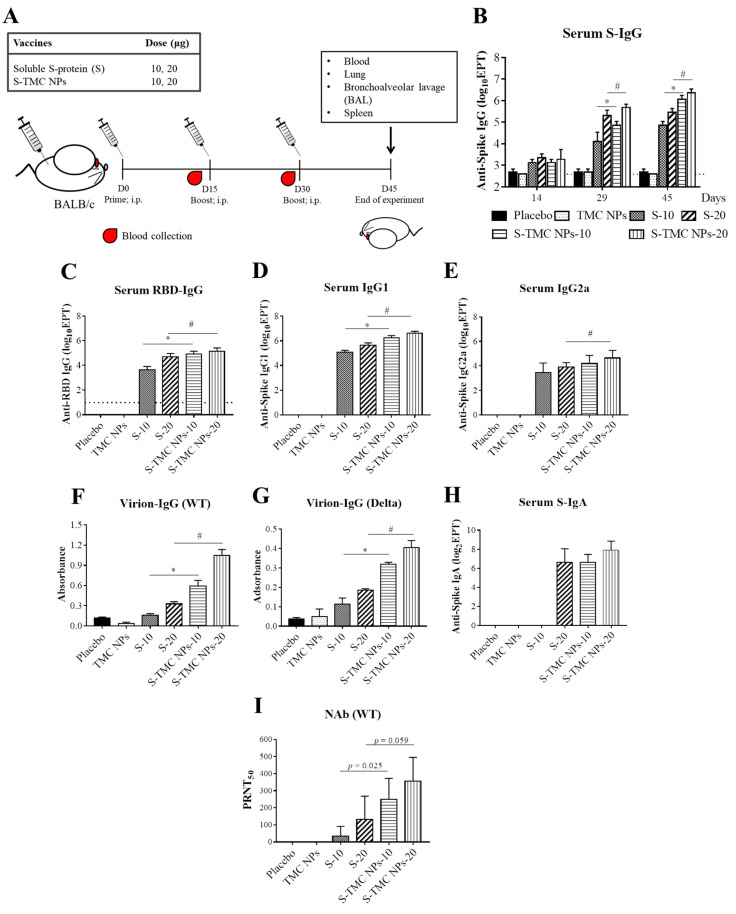
Figure 3.
Systemic humoral responses to soluble S-protein or S-TMC NPs. Mice were immunized intraperitoneally with three doses (2 weeks apart) of soluble S-protein (S) or S-TMC NPs (10 or 20 μg/dose). By Day 45 after immunization, samples from immunized mice, including blood, lungs, BALs and spleens, were harvested (A). Sera of immunized mice on Days 14, 29 and 45 were subjected to measurement of S-specific IgG by indirect ELISA (B). Sera on Day 45 were analyzed for RBD-specific IgG (C), S-specific IgG1 (D) and IgG2a (E) antibody ELISA assays. The levels of SARS-CoV-2-binding antibodies (Virion-IgG) in sera at a dilution of 1:100 were determined by capture ELISA against wild-type (WT) (F) and Delta variant viruses (G). IgA titers specific to purified S-protein were determined by indirect ELISA (H). The titers of serum neutralizing antibodies against SARS-CoV-2 were quantified by PRNT (I). Data are presented as means ± SD (n = 4); * and # indicate a significant difference between soluble S-protein and S-TMC NPs at 10 and 20 μg/dose, respectively (p < 0.05). Dotted line indicates the limit of detection (LOD) of the assay.