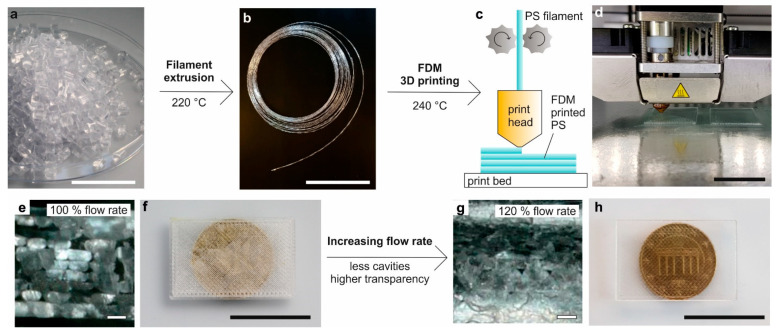
Figure 1.
Principle of FDM printing of transparent PS. (a) From commercially available PS granules (scale bar 2 cm), a continuous, windable filament (b) with a mean diameter of 2.6 mm was prepared by continuous extrusion using a twin-screw extruder (scale bar 20 cm). (c) The filament was used to 3D print transparent PS components on a commercially available FDM printer. (d) FDM printing of a planar transparent PS substrate (scale bar 2 cm). (e) Cross-section of a PS substrate that was FDM printed with a material extrusion flow rate of 100%. The strands are not completely fused together resulting in air inclusions (scale bar 200 µm). (f) A 1.1 mm-thick PS substrate that was FDM printed with 100% flow rate. The air inclusions decrease the transparency (scale bar 2 cm). (g) Increasing the flow rate to 120% yields a higher density and substantially reduced the amount of air inclusions (scale bar 200 µm). (h) A 1.1 mm-thick PS substrate that was FDM printed with a flow rate of 120%. Due to the decreased amount of air inclusions the transparency is significantly increased (scale bar 2 cm).