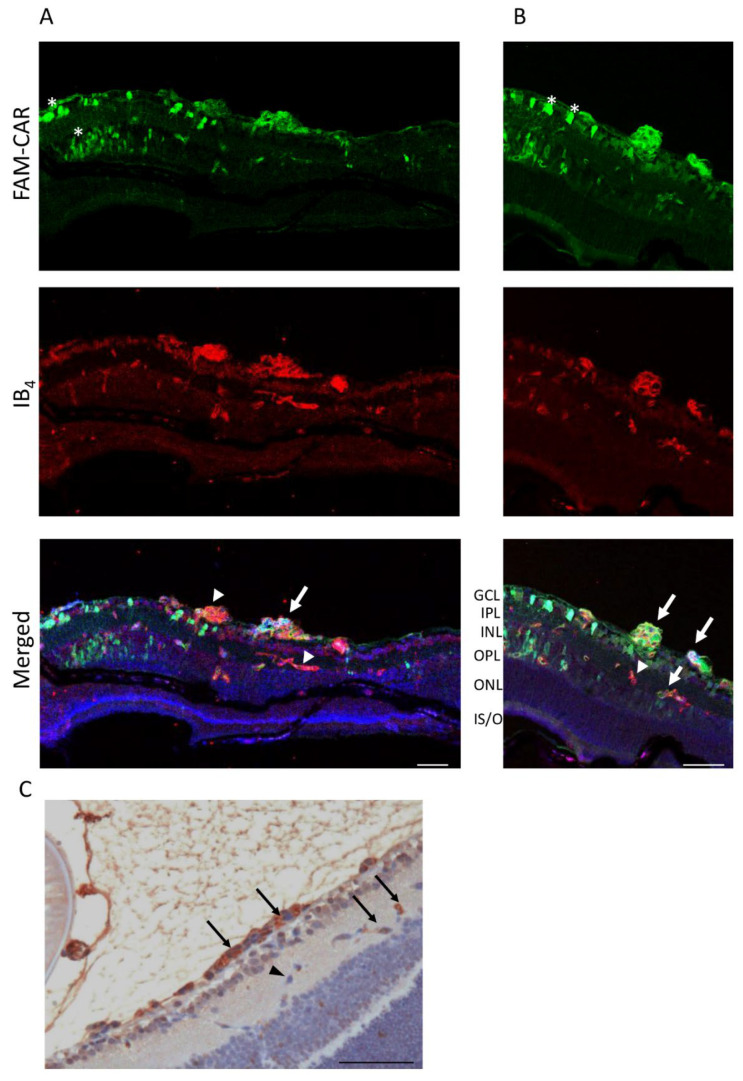
Figure 5.
Intravitreally administered CAR-peptide binds to preretinal tufts and to the blood vessels deeper in the retina. The CAR peptide was administered intravitreously. Whole eye cross sections were stained with Isolectin B4 to label the blood vessels (in red) and the FAM-conjugated CAR-peptide is visible in green (A,B). The CAR-peptide was seen in the blood vessels (arrows) in different retinal layers, while some of the retinal blood vessels remained negative for CAR homing (arrowheads). CAR-homing was also seen in the neural retina, especially in GCL and INL layers (asterisks). Retina cross sections were also stained with anti-FITC antibody and the immunohistochemical signal was imaged by light microscope (C). The staining revealed strong CAR peptide homing/binding to preretinal neovascular tufts, but also some blood vessels in the deeper retina (arrows (C). (N = 2) GCL, ganglion cell layer; IPL, inner plexiform layer; INL, inner nuclear layer; OPL, outer plexiform layer; ONL, outer nuclear layer; IS/OS, inner and outer segments. Scale bars represent 50 µm (A–C).