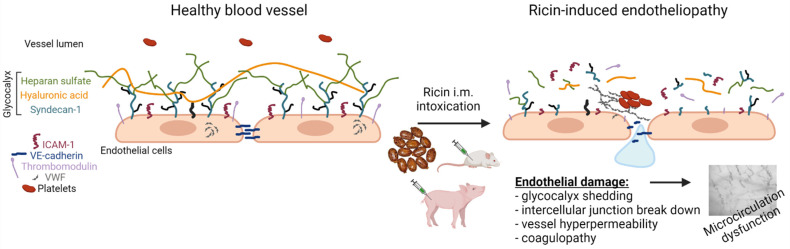
Figure 7.
Schematic representation of ricin-induced vascular damage following i.m. exposure of mice and swine. Following ricin intoxication, the vascular endothelium underwent pathophysiological changes, such as degradation of various components of the glycocalyx (syndecan-1, HS and HA), the release of thrombomodulin and ICAM-1, exposure of VWF to the bloodstream and breakdown of VE-cadherin between adjacent endothelial cells. As a consequence of these events, widespread hemorrhages, coagulopathy, vascular hyperpermeability and eventually microvasculature malfunction were detected. Created with BioRender.com.