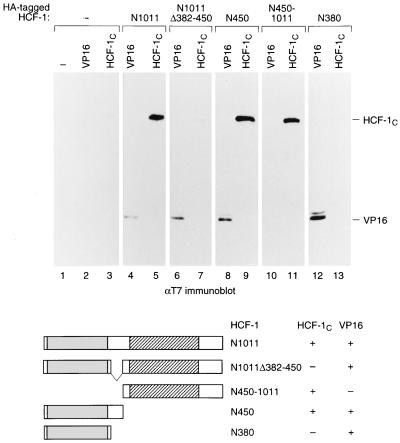
FIG. 2.
HCF-1 contains two N-terminal domains that can mediate association with the C terminus. Extracts were prepared from 293 cells transfected with 5 μg of expression plasmids encoding HA-tagged derivatives of the HCF-1N subunit and with 2 μg of expression plasmids encoding a T7 epitope-tagged version of either VP16ΔC (VP16) or the HCF-1C subunit. HA-tagged polypeptides were recovered by immunoprecipitation with an αHA monoclonal antibody, resolved on an SDS–8% polyacrylamide gel, and immunoblotted with an αT7 tag antibody (Novagen) to detect coimmunoprecipitated VP16 or HCF-1C protein. The HA-tagged polypeptides were as follows: mock (lanes 1 to 3), HCF-1N1011 (lanes 4 and 5), HCF-1N1011Δ382–450 (lanes 6 and 7), HCF-1N450 (lanes 8 and 9), HCF-1N450–1011 (lanes 10 and 11), and HCF-1N380 (lanes 12 and 13). The structures of HCF-1N and its derivatives used for coimmunoprecipitation are shown schematically below. The ability (+) or inability (−) of each amino-terminal fragment to interact with VP16 or HCF-1C is indicated.