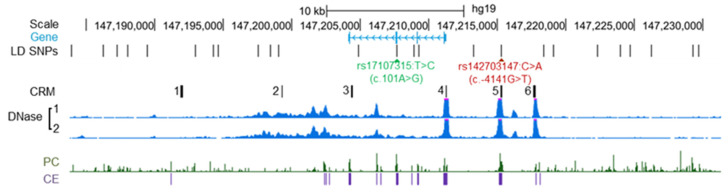
Figure 2.
Illustration of the SPINK1 locus, the locations of the SPINK1 N34S (c.101A>G; rs17107315:T>C) and c.-4141G>T (rs142703147C>A) variants, and the spatial coincidence of c.-4141G>T with regulatory features. In the “Gene” panel, the four exons of the SPINK gene are denoted by vertical lines, with the arrows indicating the direction of transcription. LD SNPs, single nucleotide polymorphisms in strong linkage disequilibrium with SPINK1 c.101A>G. It should be noted that only 24 of the 25 LD SNPs are shown in the Figure, the variant that was not shown, rs138251740A>G (located further downstream of chr5:147,230,000), is neither located within a putative PTF1L−HNF1A CRM nor within a region showing strong evolutionary conservation and high chromatin accessibility. CRM, cis-regulatory modules harboring binding sites for transcription factors HNF1A and PTF1L. DNase, DNase I-accessible DNA regions in the pancreatic tissues of two donors as determined by DNase-seq. PC and CE, Placental Mammal Conservation by PhastCons (PC) and Placental Mammal Conserved Elements (CE) were obtained from the UCSC Genome Browser. The Figure was adapted from our work [18] with permission (Copyright 2021 Wiley Periodicals LLC).