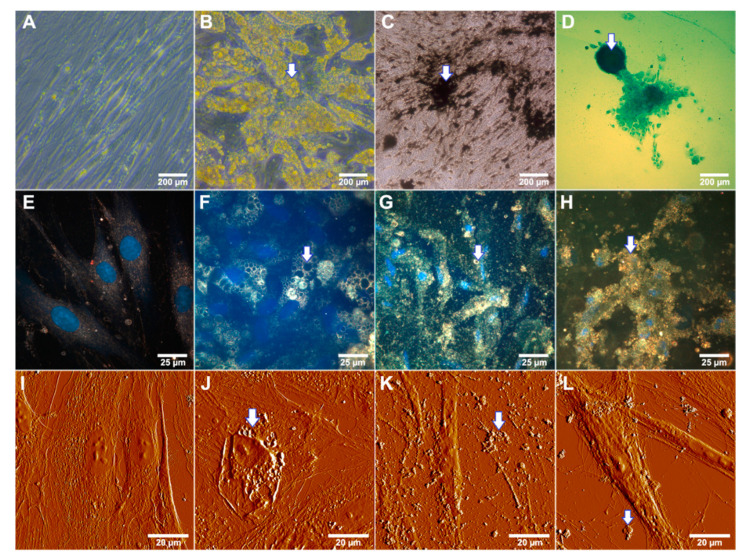
Figure 3.
Differentiation potential of equine adipose derived mesenchymal stem cells after 14 d incubation in differentiating media. Arrows indicate characteristic changes of cellular morphology. (A)—cells incubated in the presence of α-MEM (negative control); (B)—cells grown under adipogenic conditions (note a huge amount of yellow colored lipid droplets); (C)—von Kossa staining of cells differentiated to the osteoblasts under osteogenic conditions (note the black stained calcium accretion); (D)—alcian blue staining of cells differentiated to the chondrocyte lineage in chondrogenic medium (polyanionic glycosaminoglycan chains of proteoglycans visualized as a blue agglomerate). (E–L)—Label-free visualization of differentiated MSCs under specific conditions, (E–H)—dark-field microscopy; (E)—control (α-MEM), (F)—adipogenic differentiation, (G)—osteogenic differentiation, (H)—chondrogenic differentiation; nuclei were stained with DAPI and detected using fluorescence mode; (I–L)—AFM detection; (I)—control, (J)—adipogenic differentiation, (K)—osteogenic differentiation, (L)—chondrogenic differentiation.