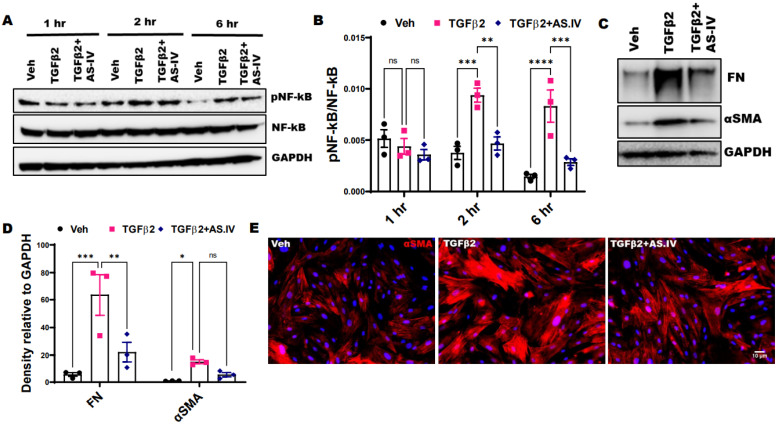
Figure 3.
AS.IV treatment attenuates TGFβ2 induced NF-κB activation and αSMA expression. (A,B) Western blot (A) and its densitometric (B) analysis of TM3 cell lysates treated with vehicle, TGFβ2 (5 ng/mL) and TGFβ2 plus AS.IV (100 µM) at various time points (1, 2 and 6 h). The TGFβ2 significantly increased pNF-κB/NF-κB levels at 2 & 6 h after the treatment, indicating the activation of NF-κB signaling. The AS.IV co-treatment significantly suppressed the TGFβ2 induced NF-κB activation (n = 3 replicates, data represented as mean ± SEM, 2-way ANOVA, Tukey’s multiple comparisons test, ** p < 0.01, *** p < 0.001, **** p < 0.0001). (C–E) Western blot (C), its densitometric (D) and immunostaining (E) analysis of primary human TM cells treated with vehicle, TGFβ2 (5 ng/mL) and TGFβ2 plus AS.IV (100 µM) for 3 days. The TGFβ2 treatment significantly increased the αSMA expression whereas AS.IV co-treatment prominently suppressed. Scale bar 10 µm. (n = 3 cell strains, data represented as mean ± SEM, 2-way ANOVA, sidak’s multiple comparisons test, * p < 0.05, ** p < 0.01, *** p < 0.001).