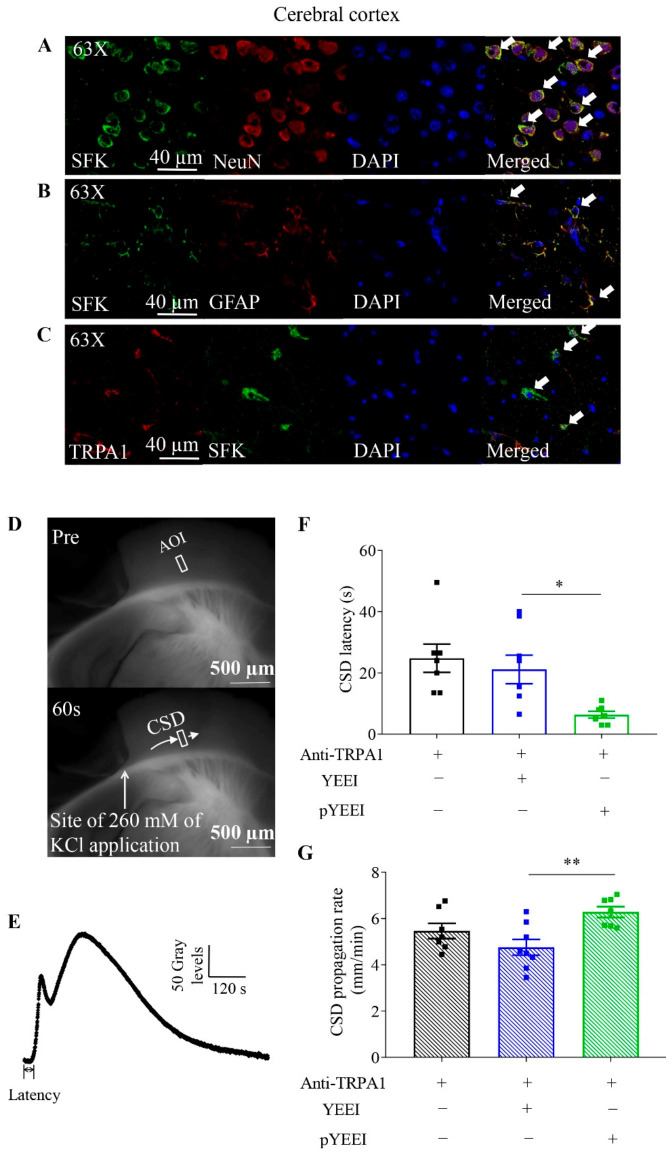
Figure 1.
Co-localization of TRPA1 and SFKs, and effects of pYEEI, the SFKs activator, on the anti-TRPA1 antibody-reduced cortical susceptibility to CSD in the mouse brain slice. (A,B) Representative images of expression of SFKs in neurons and astrocytes of mouse cerebral cortices. (C) Representative images of co-localization of TRPA1 and SFKs in mouse cerebral cortices. Staining with DAPI indicated nucleus as shown in blue; staining with the anti-TRPA1 antibody was shown in red; staining with the anti-NeuN antibody indicated neurons and staining with the anti-GFAP antibody indicated astrocytes as shown in green. Double immune-labeling showed expression of SFKs in neurons and astrocytes of mouse cerebral cortices or co-expression of TRPA1 and SFKs in mouse cerebral cortices (white arrows, n = 3 per group). (D) Representative images of the coronal slice of mouse brain before (upper) and after (lower) CSD induced by ejection of 260 mM KCl in the cerebral cortical region. The same area of interest (AOI) along CSD wave front (pointed by the short arrow) was selected and used for all images. (E) The averaged gray level within the AOI was plotted against time to generate the CSD curve. (F,G) Effects of 0.015 µM anti-TRPA1 antibody (Anti-TRPA1) (n = 7), 0.015 µM anti-TRPA1 antibody + 0.1 µM pYEEI (n = 7), or 0.015 µM anti-TRPA1 antibody + 0.1 µM YEEI (n = 8) on CSD latency (seconds, s) and CSD propagation rate (mm/minute, mm/min) in mouse brain slices. Group data were presented as mean ± SEM. Two-tailed unpaired t-test was used for comparison between pYEEI and YEEI group in the presence of anti-TRPA1 antibody. Significance differences were shown as * p < 0.05, ** p < 0.01.